American psychologist Abraham Maslow introduced Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs in his paper “A Theory of Human Motivation.” This theory says that each human has five levels of needs based on their importance, and achieving the needs of all levels leads to complete satisfaction.
Definition: Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs explains what motivates a human being and suggests that humans will fulfill their basic needs before moving on to the next level.
What is Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs?
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs chart shows basic to advanced human requirements that help them achieve an overall sense of satisfaction. The hierarchy is represented through a pyramid structure that starts with basic needs at the bottom and goes up towards self-actualization needs at the top.
Such needs, according to PMI, can be essential in project management to ensure employee motivation and satisfaction.
The Five Basic Needs in Maslow’s Hierarchy
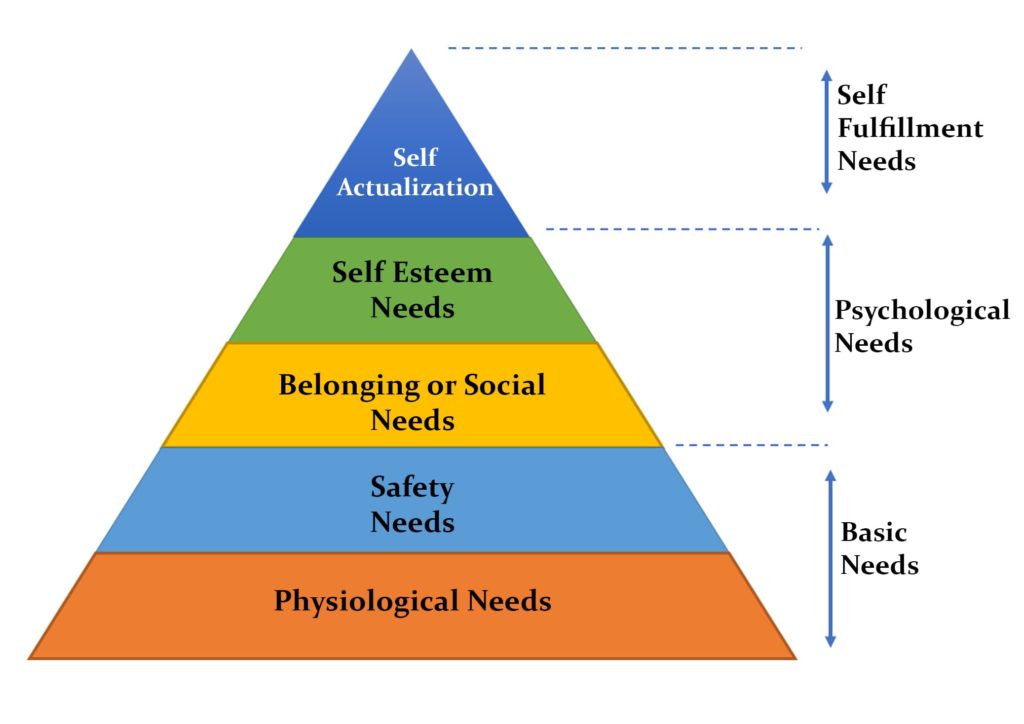
#1. Physiological Needs
Physiological needs are the most basic needs a human must fulfill to survive. The human body struggles to operate efficiently if these needs are not satisfied. Hence, physiological needs are the most critical and primary needs in the hierarchy.
These needs include the basic need for air, shelter, clothing, controlled temperature, water, sleep, nutrition, etc.
#2. Safety Needs
Safety needs, also called security needs, are the second-most vital needs in Maslow’s hierarchy.
Once individuals fulfill their physiological needs, they move on to securing themselves physically, mentally, environmentally, and emotionally.
This level of needs includes protections like job security, family protection, health, etc.
#3. Belongingness Needs
Belongingness needs, also known as social needs, include a human’s need for affection, love, belongingness, and emotional strength from family, friends, loved ones, and society.
These needs include friendship, romantic attachments, social groups, acceptance, love, and care that help in strengthening an individual’s emotional relationships. All these needs combined help protect the individual against depression, anxiety, sadness, helplessness, and loneliness.
#4. Esteem Needs
The fourth level in the hierarchy of needs is esteem needs, which includes appreciation, respect, and acknowledgment. Once a human has achieved physiological, safety, and social needs, they move on to esteem needs that help them stay motivated.
These needs include internal esteem needs like self-confidence, self-respect, competence, freedom, and sense of achievement, along with external esteem needs like social recognition, attention, power, admiration from others, acknowledgment, and status.
Humans like to be recognized to enhance their worth. When individuals get value from others, they feel like their existence matters.
#5. Self-Actualization Needs
Self-actualization is the top-level need in Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs. At this level, the individual seeks to realize their true potential, grow and experience self-fulfillment to achieve the maximum level of satisfaction.
These needs include self-contentment, desire to gain more knowledge, self-growth, social service, becoming more appealing, and exploiting their talents. This need is hard to satisfy as individuals keep growing as opportunities come to them, and hence, one never stops utilizing their potential.
Expanded Needs in Maslow’s Hierarchy
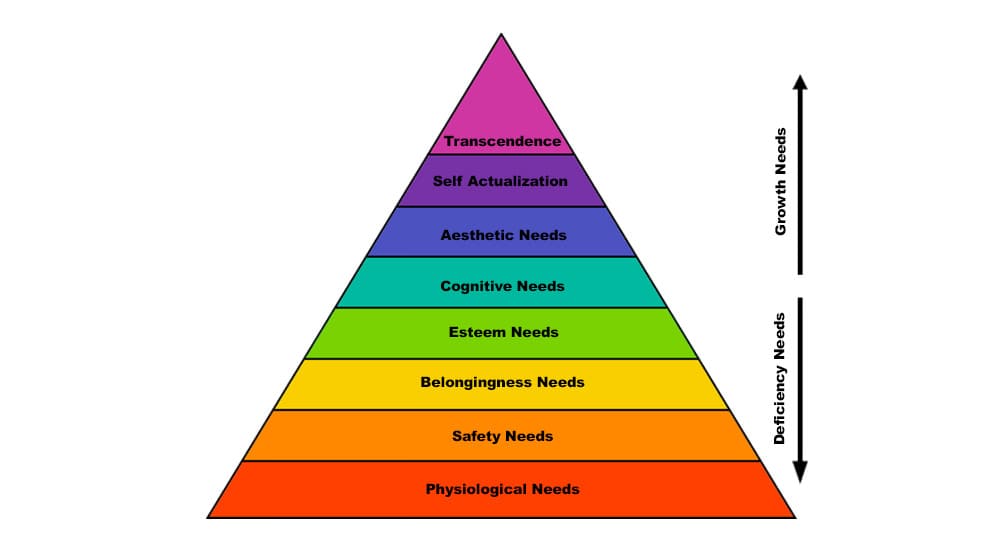
Maslow’s original model of the five needs was expanded in 1970 to include three more needs. These three needs are cognitive, aesthetic, and transcendence needs. The cognitive and aesthetic needs come after the esteem needs but before the self-actualization needs.
The transcendence needs are the topmost level of the needs pyramid and suggest the maximum level of satisfaction.
#1. Cognitive Needs
Cognitive needs refer to increasing an individual’s intelligence through curiosity and inquisitiveness. After achieving their esteem needs, humans move on to fulfilling their needs to learn, understand, explore, solve problems, and discover things to understand the world better.
The need to learn more helps individuals get rid of confusion, existential crisis, and identity uncertainty.
#2. Aesthetic Needs
Aesthetic needs are a human’s need to search for beauty and appreciation. Humans look for aesthetic images and beauty around them to absorb attractiveness and feel beautiful. This need includes allowing humans to feel connected with the environment and extract nature’s beauty to feel intimate with their surroundings.
#3. Transcendence Needs
Transcending means to rise above. The transcendence need is the topmost level of satisfaction in Maslow’s eight-level Hierarchy of Needs. It is an individual’s need to achieve meaning and purpose in their lives.
According to this theory, humans transcend their concerns to see a higher perspective in a situation to bring out strong emotions like peace, joy, self-awareness, and happiness. The motivation at the transcendence level occurs beyond the personal self and enables individuals to witness peak experiences in their lives.
Example of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Each person’s motivation and satisfaction level depend on their hierarchy stage. What may be satisfactory for a person at the physiological needs level may not be satisfactory for someone at the esteem needs level.
Let’s understand this with an example.
Consider two people, A and B. Person A visits a foreign country and gets lost while trekking. This person has no food, water, shelter, or clothes. The weather is cold, and he is out of money. This individual is currently pursuing the physiological needs level and is only concerned with finding shelter, food, and water.
At this point, person A will not care about safety, social, esteem, or self-actualization. He needs basic needs and a way to go home. This will satisfy him.
On the other hand, person B is a big corporation employee, financially strong, and has a loving family. Since the person is financially secure, his food, water, shelter, clothing, security, and other primary needs are fulfilled. This person also has a social circle with his office peers and spends time with his family, fulfilling his social and esteem needs.
Hence, the next level that will help the person be motivated is the self-actualization need. The needs for person B consist of personal growth, a high ability to solve problems, and the epitome of happiness in his personal and professional life. After achieving these needs, the person will be completely satisfied and motivated to continue living as usual.
Implications of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Theory for Managers
Managers are responsible for ensuring that the needs in Maslow’s Hierarchy are fulfilled for their employees to be motivated and perform better.
Here is how managers can ensure employees’ needs are fulfilled:
Managers can help fulfill physiological needs by providing good salaries to employees to maintain a decent lifestyle. Bonuses and work assignments also help motivate employees to work harder. Breaks should also be given for the employees to relax, eat, and rejuvenate themselves while working.
Managers should provide employees with a safe working environment to guarantee physical safety. Financial security can be given by providing employees with retirement benefits, compensatory layoff salaries, provident funds, gratuities, etc., which help employees become financially secure during and after employment.
To fulfill social needs, managers can allow employees to collaborate. Employees should be encouraged to work as a team and allowed to meet with management through workshops, social gatherings, etc.
Managers should always show appreciation for employees when they perform well and motivate them to do better when they perform under expectations.
Benefits should be given when targets are achieved early, along with promotions and increments to satisfy esteem needs. Praise from managers in front of the team motivates employees. Managers should show faith in their employees even when they perform below expectations.
Moving onto the more advanced levels of satisfaction, managers can fulfill the employees’ cognitive needs by letting them attend informative workshops, allowing them to discover new ideas and get their questions answered. Providing employees with professional freedom helps in satisfying cognitive needs as it lets employees expand their outlook on work-related things.
Next, fulfilling aesthetic needs depends on the beauty that employees are surrounded by. Managers can ensure that the aesthetic needs are satisfied by providing employees with a pleasing and calm working environment. This includes having a clean workspace that is bright and beautiful, enabling employees to enjoy work as soon as they enter the workplace.
Managers can fulfill their employee’s self-actualization needs by giving employees challenges in the workplace to allow them to showcase their competencies and skills. Challenging tasks lead the employees to realize their full potential and worth. Growth opportunities like leading a team or organizing a formal event help satisfy the employees’ self-actualization needs.
Last but not least, managers can help employees fulfill their transcendent needs by providing them with activities that go beyond the normal routine of self-motivation. Such activities can include corporate social responsibility, acts of service to the underprivileged, visits to different places, and more.
Pros of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Theory
- This theory has a strong significance in the business world as it helps motivate employees in the workplace.
- The theory summarizes human needs that help interpret how a human reacts and behaves before and after achieving each needs level.
- The needs theory can help businesses focus their product or service advertising based on specific human needs that their target market might have.
- Since Maslow’s theory is direct and uncomplicated, it helps understand the motivations and incentives behind human behavior.
- Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs summarizes human nature and how people are motivated by basic and advanced levels of needs in their professional and personal lives.
Cons of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Theory
- Since needs are subjective, it is impossible to realize the actual level of need that must be attained to move on to the next level.
- All employees in an organization are governed differently. The same motivator does not drive all employees, and this makes it difficult to satisfy all employees.
- Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs is not empirical since the satisfactory level cannot be checked.
- The model is Western, and hence, the cultural foundation does not make it a universally accepted theory.
Conclusion
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs represents one of the most important psychological aspects of a human’s motivational behavior. It focuses on developing physically and mentally healthy individuals. Irrespective of the criticisms, the theory provides in-depth information about human needs and how each individual reacts to those needs. Even if an individual does not place the needs in the same order as Maslow, all needs play a vital role in the individual’s overall happiness and motivation.
