Multilevel marketing (MLM) goes by many names such as network marketing, referral marketing and direct selling are a few. MLM is a business model where independent distributors earn money by selling products and recruiting others to do the same. MLM companies promise flexible schedules and the chance to build a team, but they also come with risks and controversy.
This blog post explains how MLM works, shares recent statistics and offers practical advice for anyone considering joining an MLM.
What is Multilevel Marketing?
Multilevel marketing is a form of direct sales. People sign up as independent distributors for a company’s product or service. They earn income in two ways: by selling goods to customers and by recruiting new distributors. Each distributor has a “downline,” the people they bring into the organization, and typically receives a small percentage of the downline’s sales. This structure can continue for several levels, which is why it is called multilevel marketing.
MLM models rely heavily on personal relationships. Distributors often pitch products to friends, family and social media followers. They may host parties, hold online events or reach out through direct messages. Because distributors act as both salespeople and recruiters, companies can expand quickly without large advertising budgets.
A Brief History of MLM
Direct selling has existed for more than a century. In the 1940s and 1950s companies like Nutrilite and Amway introduced the idea of rewarding customers who brought in new buyers. This compensation system evolved into today’s multilevel marketing. During the 1970s and 1980s, MLM spread globally as companies like Tupperware and Mary Kay expanded. With the rise of social media in the 2010s, MLM found new channels for recruitment and product promotion.
Direct selling has remained a significant industry. According to the World Federation of Direct Selling Associations (WFDSA), global retail sales through direct selling were nearly unchanged in 2024, declining by only 0.05 % compared with the previous year. This stability after earlier declines indicates that the market may be recovering from pandemic‑related turbulence.
How Does Multilevel Marketing Work?
MLM companies offer distributors a chance to start a small business with modest startup costs.
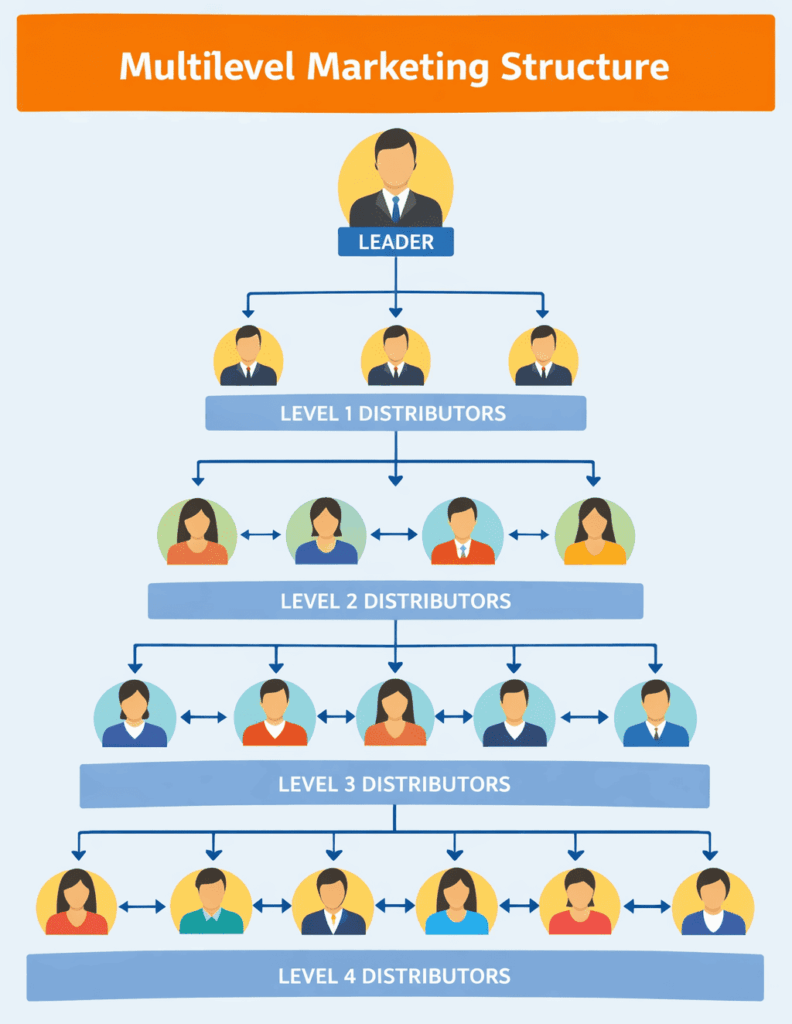
The process looks like this:
- Join the company. An individual signs up through an existing distributor, often paying an initial fee and purchasing a starter kit of products.
- Sell products or services. The new distributor markets products to family, friends or online followers. They earn commissions on these sales.
- Recruit others. The distributor invites other people to join. When those recruits sell products, the original distributor earns a percentage of their sales. This repeats through multiple levels.
- Build a team. As the downline grows, the distributor may earn bonuses or higher commissions based on the overall volume generated by their team.
The diagram below illustrates a simple MLM structure, with one distributor at the top and several levels of recruits beneath. Each circle represents a person; arrows show the flow of recruitment and commissions.
This structure illustrates why MLMs can grow quickly. Each recruit becomes both a customer and a salesperson, and they are motivated to recruit others. However, the model also creates pressure to recruit continuously because profits often depend more on recruitment than on product sales.
MLM Vs Pyramid Scheme
The line between a legitimate MLM and an illegal pyramid scheme can seem blurry.
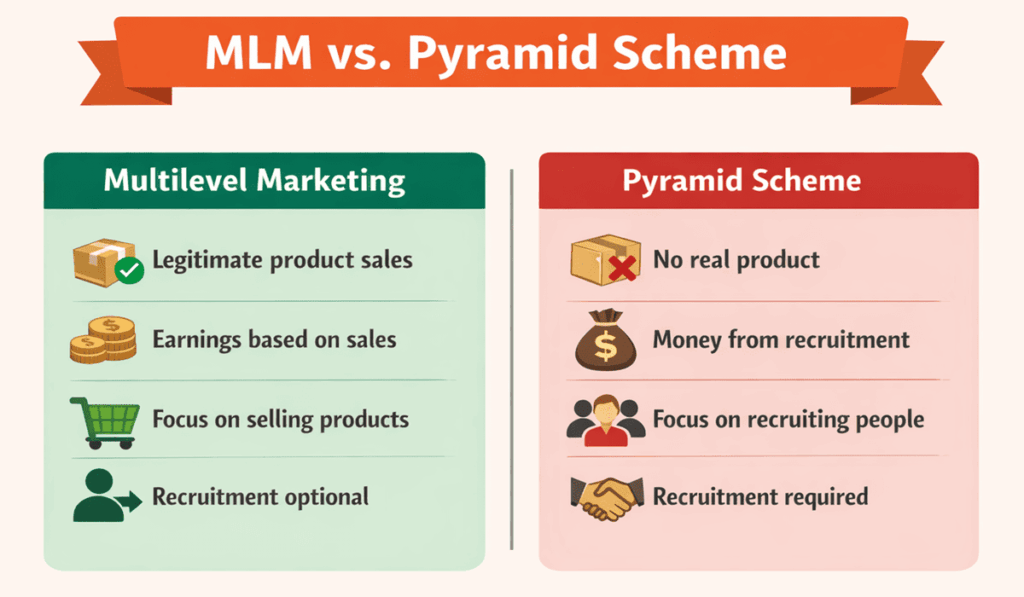
Both involve recruitment, but there are key differences:
- Real product or service: Legitimate MLMs sell genuine goods and services, and revenue comes primarily from product sales. In a pyramid scheme the main “product” is the right to recruit others.
- Earnings based on sales: In MLM the bulk of earnings should come from selling to real customers. Pyramid schemes reward members mainly for bringing in new recruits.
- Regulatory oversight: MLM companies are subject to consumer protection laws and must provide income disclosures. Pyramid schemes are illegal and often collapse, leaving most participants with losses.
The following infographic highlights these distinctions side by side.
Pros of Multilevel Marketing
Supporters say that MLMs offer an accessible path to entrepreneurship. Some of the potential advantages include:
- Low startup costs: Many companies allow individuals to join for a small initial fee and a starter kit. Compared with traditional franchises or retail businesses, the barrier to entry is lower.
- Flexible schedule: Distributors often work from home and set their own hours. This flexibility appeals to people who need a side income or who have family responsibilities.
- Potential for high earnings: Experienced distributors who build large teams can earn significant income. Because commissions and bonuses are tied to group sales, there is no fixed ceiling.
- Personal development: MLMs often offer training on sales, public speaking and leadership. Distributors may gain communication skills, confidence and a network of contacts.
- Community and support: Many MLMs emphasize mentorship and teamwork. New recruits receive guidance from their sponsors and may find a sense of community.
Cons and Risks
Despite these advantages, MLMs carry real risks. Critics note several drawbacks:
- Low earnings for most participants: A FTC analysis of 70 income disclosure statements found that most participants made less than $1,000 per year, or about $84 per month. In at least 17 MLMs, most participants earned nothing at all.
- Pressure to recruit: Because earnings often depend on the size of the downline, distributors may feel compelled to recruit friends and family. This can strain relationships and lead to disappointment when recruits do not sell products.
- Inventory loading: Some MLMs require distributors to buy large quantities of products in advance. Unsold inventory becomes a financial burden.
- Misleading income claims: Promotional materials may highlight the earnings of top performers while downplaying the experiences of the majority. Consumers should read income disclosures carefully.
- Legal uncertainty: Regulators continue to scrutinize MLMs. If a company operates more like a pyramid scheme, participants risk losing their investment and could face legal consequences.
Recent Statistics and Industry Trends
In addition to the earnings data mentioned above, the WFDSA report provides insight into the direct selling industry:
- Billion‑dollar markets: In 2024 there were 21 markets worldwide with retail sales exceeding one billion dollars, representing 92% of global sales. These markets include the United States, Germany, China, Korea and Malaysia.
- Number of independent contractors: The global direct selling workforce consisted of about 104.3 million independent contractors, with women making up roughly 72.1% of that group.
- Regional distribution: The Asia–Pacific region accounted for 40.3% of global direct selling sales, followed by the Americas at 37.3% and Europe at 21.6%.
These figures suggest that direct selling remains a significant economic sector, particularly in Asia and the Americas. However, the concentration of sales in a small number of countries means competition is intense.
How to Evaluate an MLM Opportunity
If you are considering joining an MLM, ask yourself these questions:
- What is the product? Is it something you genuinely like and can sell to others? Avoid companies that focus more on recruitment than on real products.
- How is income earned? Read the compensation plan. Income should come mainly from sales, not from signing up new distributors.
- Are income disclosures available? Reputable MLMs publish disclosure statements. Use these to see what typical participants earn.
- What are the costs? Account for initial fees, inventory purchases and marketing expenses. Compare potential profits with these costs.
- Is there a buyback policy? Legitimate companies allow you to return unsold products within a reasonable period.
- What is the company’s reputation? Look for third‑party reviews and check if the company is a member of a recognized direct selling association.
By taking time to research and by talking to current and former distributors, you can avoid scams and make an informed decision.
Real‑World Examples of MLM Companies
Several companies are commonly associated with multilevel marketing. Each has a different product focus and business history:
- Amway: Established in 1959, Amway sells health, beauty and home care products. It operates in more than 100 countries and is one of the largest MLMs.
- Mary Kay: Founded in 1963, Mary Kay specializes in cosmetics and skin‑care products. The company emphasizes training and recognition for its consultants.
- Herbalife: Known for nutritional supplements and weight‑management products, Herbalife has faced regulatory scrutiny but remains a major player in the direct selling industry.
- Tupperware: Famous for its plastic food containers, Tupperware pioneered home party sales and continues to use a direct selling model.
- Ambit Energy: A newer entrant focused on energy services, Ambit allows customers in certain U.S. markets to switch electricity providers through a network marketing structure.
These examples illustrate the diversity of MLM products. However, success stories are often the exception rather than the rule. Always look beyond marketing materials and examine the facts.
Legal Considerations and Consumer Protection
The FTC’s Business Guidance Concerning Multi‑Level Marketing outlines best practices for MLM companies and participants. The agency warns that income disclosures can be misleading and encourages consumers to scrutinize claims. Before joining any direct selling program, review national regulations and ensure the business complies with local laws. Be cautious of “opportunities” that guarantee quick wealth or require large upfront payments.
FAQs
Q1. Is multilevel marketing illegal?
No. Legitimate MLMs sell real products and comply with consumer protection laws. Pyramid schemes, which focus on recruitment rather than sales, are illegal.
Q2. Can you really make money in an MLM?
Some top distributors earn significant income, but the FTC notes that most participants make less than $1,000 per year. Success depends on product demand, sales skill and the size of your network.
Q3. How do I avoid a pyramid scheme?
Look for companies that emphasize product sales over recruitment, provide clear income disclosures and offer buyback policies. Avoid programs that require large upfront payments or promise unrealistic returns.
Conclusion
Multilevel marketing offers an accessible entry into the world of business. When done responsibly, it can provide supplemental income, personal growth and a supportive community. Yet the risks are real: most participants earn little or nothing, and some companies operate illegally. Understanding how MLM works, recognizing the difference between legitimate operations and pyramid schemes, and asking the right questions can help you make an informed decision