Smaller teams are much easier to manage because you know them personally and can ensure they know their roles and responsibilities.
However, managing a growing team efficiently becomes more difficult, leading to compromised organization and potential conflicts.
Therefore, you will use the RACI Chart to solve these issues. The RACI Chart is a simple tool that the PMBOK Guide describes in the plan resource management process.
The RACI Chart is also known as a RACI Matrix or Linear Responsibility Chart (LRC).
What is a RACI Chart?
A RACI Chart is a type of Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) that visually shows the roles and tasks assigned to each team member.
It identifies the roles and responsibilities of the individuals in tasks and projects. This chart can help you determine who is assigned to what in particular.
A RACI Chart is useful at all levels of project management; if the project is large, you can create it to connect high-level work packages with the project team, group, or unit. Also, you can make a low-level RACI Chart within teams, groups, or units and use it to connect the tasks or activities with each individual.
What Does RACI Mean?
RACI stands for Responsible, Accountable, Consult, and Informed.
Responsible
This team member is responsible for carrying out the activities required to complete the task. A task must have at least one responsible team member who is in charge of decision-making, but it can have more than one responsible team member.
Accountable
This team member is accountable for the job. In a small project, a team member can be responsible and accountable for the task, but it is a good idea to separate these roles for larger projects. This team member is answerable to the project manager about the progress and review of the tasks.
Remember that all tasks must have a responsible and accountable team member. Though a task can have multiple responsible parties, it is best to have only one who is accountable to individual tasks to avoid confusion and allow faster decision-making. If a task is big or complex, there can be more accountable team members.
Consult
Consulting team members provide input and help define each task. These individuals may be directly impacted by the deliverable being completed, and they will interface with you, the project manager, when presenting the deliverable.
These team members must be contacted if any technical clarification is needed or if the deliverable must be changed or reviewed.
Responsible and consulting team members must have two-way communication.
Informed
These team members have no direct involvement in a particular task but are kept informed about progress. They have the potential to be a replacement if another member leaves the project or is assigned somewhere else.
There is one-way communication with this group of team members.
Benefits of a RACI Matrix
A RACI Matrix is a powerful tool for managing projects effectively. It is help to you as follows:
- Ease of Use and Readability: A RACI Chart is straightforward to create and interpret, providing a clear and concise view of roles and responsibilities.
- Workload Management: It helps monitor and manage team members’ workloads, ensuring balance and efficiency. It distributes tasks equitably to prevent overburdening any individual.
- Role Clarity: This clearly identifies who is responsible, accountable, consulted, and informed for each task, avoiding confusion and misunderstandings. It also ensures the right person is contacted for specific tasks, streamlining communication.
- Task and Role Optimization: Eliminates unnecessary tasks by focusing on what is essential and assigning roles appropriately. It helps visualize responsibility and accountability, ensuring everyone knows their role.
- Conflict Prevention and Resolution: Defining roles and expectations upfront reduces potential conflicts over responsibilities. It facilitates smoother handoffs between tasks or phases in a project.
- Resource and Communication Efficiency: It enables project managers to redistribute work effectively if needed. It also acts as an excellent communication tool, enhancing collaboration among team members.
- Faster Decision-Making: Helps project managers quickly address concerns with the appropriate team member, leading to timely resolutions.
- Improved Resource Allocation: This method avoids conflicting assignments by clearly delineating responsibilities. It also helps team members step into leadership roles, fostering accountability and ownership.
Drawbacks of a RACI Chart
While a RACI Chart offers many benefits, it also has certain drawbacks and limitations:
- Complexity in Large Projects: RACI Charts can become overly detailed and hard to manage for complex projects with numerous tasks and team members. Identifying the individual responsible for a given task may become challenging amidst the extensive information.
- Lack of Flexibility: RACI Charts are not easily adaptable to frequent assignments or team role changes, making them less effective in dynamic project environments.
- Potential Role Confusion: If responsibility and accountability are not clearly defined, there is a risk of overlapping roles or ambiguity. Misunderstandings about who is responsible or accountable for tasks can hinder progress.
- Time-Consuming Setup: Creating and maintaining an accurate RACI Chart can be time-consuming, especially in projects with evolving needs or stakeholder involvement.
- Limited Insight into Task Dependencies: A RACI Chart focuses primarily on roles and responsibilities and may not adequately capture task interdependencies or workflow dynamics.
- Potential Overemphasis on Documentation: Teams may spend excessive time debating or finalizing the RACI Chart instead of focusing on task execution, leading to delays.
When Should You Use a RACI Matrix?
A RACI Matrix is a valuable tool in project management, particularly in the following scenarios:
- Tracking Team Members’ Progress: This is when you need to verify whether a specific team member is completing their assigned tasks as planned.
- Resolving Role Conflicts: If there is a conflict or ambiguity about who is responsible or accountable for a particular task, a RACI Chart can help clarify and resolve the issue.
- Reassigning Roles: When a role or responsibility needs to be transferred from one team member to another, the RACI Chart can streamline the process and prevent gaps or overlaps.
- Providing Visibility to Management: When management wants a clear view of each team member’s role, responsibilities, and contributions within the project.
- Clarifying Roles in Multi-Team Projects: In projects involving multiple teams or departments, a RACI Chart helps align everyone on who is doing what, reducing confusion.
- Onboarding New Team Members: A RACI Matrix can serve as a reference to help new team members quickly understand their responsibilities and those of others.
- Ensuring Accountability in Complex Projects: For projects with numerous stakeholders, a RACI Chart ensures accountability is assigned and tracked for every critical task.
Step-by-Step Process to Create a RACI Chart:
The steps of creating a RACI Charts are as follows:
Step 1. List the Role
First, list all the roles involved in your project, such as project manager, planning engineer, foreman, construction engineer, quality control engineer, etc.
Enter these roles in the top row of the table, as shown in the picture. You can use the names of team members instead if you choose to. Don’t forget to review the project charter, which can provide valuable information on important stakeholders.
Entering roles into the chart has advantages. For example, if a team member leaves the project, you don’t have to update the RACI Chart. On the other hand, entering names makes the project manager’s job easier when many team members share a similar role.
Step 2. List the Tasks
Review the project work, breaking it down into tasks and listing them all: developing project plans, identifying risks, testing deliverables, maintaining records, or whatever.
Once done, you can enter the information in the first vertical column, as shown in the image.
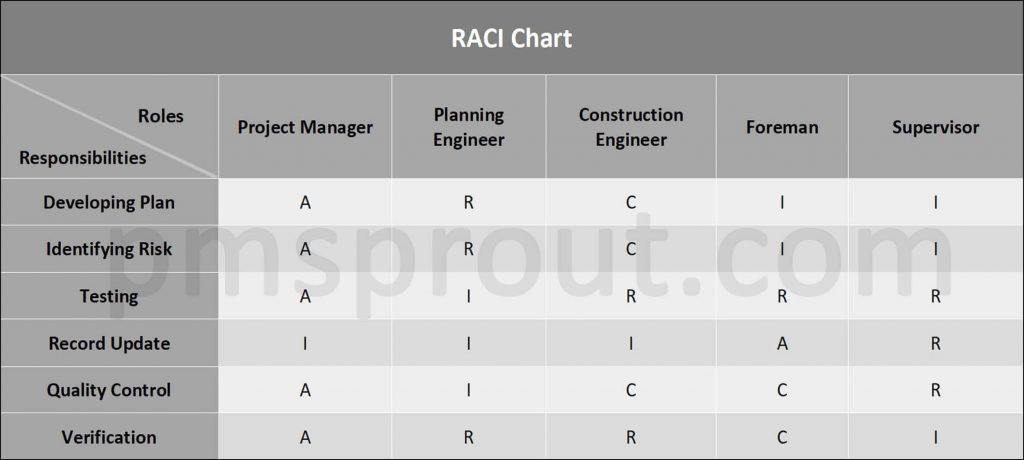
Step 3. Assign the Value
Now, for each task, you will assign a value:
- For responsible, you will use “R.”
- For accountable, you will use “A.”
- For consult, you will use “C.”
- For informed, you will use “I.”
Alternatives to a RACI Chart
Many types of Responsibility Assignment Matrixes (RAMs) are used in project management; however, they are not discussed here because they are not mentioned in the PMBOK Guide and are not necessary for the PMP exam.
Some commonly used RAMs are as follows:
- RATSI (Authority, Responsible, Task, Support, Informed)
- RASCI (Responsible, Accountable, Supportive, Consulted, Informed)
- CARS (Communicate, Approve, Responsible, Support)
- DACI (Drivers, Approver, Consulted, Informed)
- CLAIM (Contributes, Leads, Approves, Informed, Monitors)
- PACSI (Performed, Accountable, Control, Suggested, Informed)
- RAPID (Recommend, Agree, Perform, Input, Decide)
Conclusion
A RACI chart helps assign work and avoid conflicts. Stakeholders’ support is vital for a chart to be effective. Always update it as soon as any change occurs, as outdated information will nullify a RACI Chart. Make sure all stakeholders understand the terms and agree.

CLAIM the meaning of “I” is omitted. I think it stands for informed . The information is clear and easily applicable. The RACI chart is an essential for monitoring and controlling projects effectively. Thanks a million, Fahad. Keep up the great work.
Hello Rensom, thanks for letting me know about it.
CLAIM the meaning of “I” is omitted. I think it stands for informed . The information is clear and easily applicable. The RACI chart is an essential for monitoring and controlling projects effectively. Thanks a million, Fahad. Keep up the great work.
Hello Rensom, thanks for letting me know about it.
I use these charts through Primavera P6 but I cannot say those are exactly the same but the concept is the same as of RACI.
It is prepared there for all the teams working on our enterprise structure. Later, that is further sent to on-site teams but is updated from head office only for top-level executives.
A RACI chart can be designed in many ways depends on the requirements.
I use these charts through Primavera P6 but I cannot say those are exactly the same but the concept is the same as of RACI.
It is prepared there for all the teams working on our enterprise structure. Later, that is further sent to on-site teams but is updated from head office only for top-level executives.
A RACI chart can be designed in many ways depends on the requirements.