Definition: A business level strategy defines a business’s goals and policies to deliver value to customers and have a competitive advantage over competitors. It determines the direction of the business, establishes its brand, and defines how a business serves its customers.
These strategies help businesses satisfy their customers, avoid competition and achieve an edge over rivals.
Adopting the right business strategy is vital for a successful business. A business first identifies its target customers, product range, available resources, competition, market trends, capability, etc. Afterward, they can formulate the business strategy to serve the consumers well.
According to Michael Porter, a business can have three levels of strategies:
- Corporate Level Strategy
- Business Level Strategy
- Functional Level Strategy
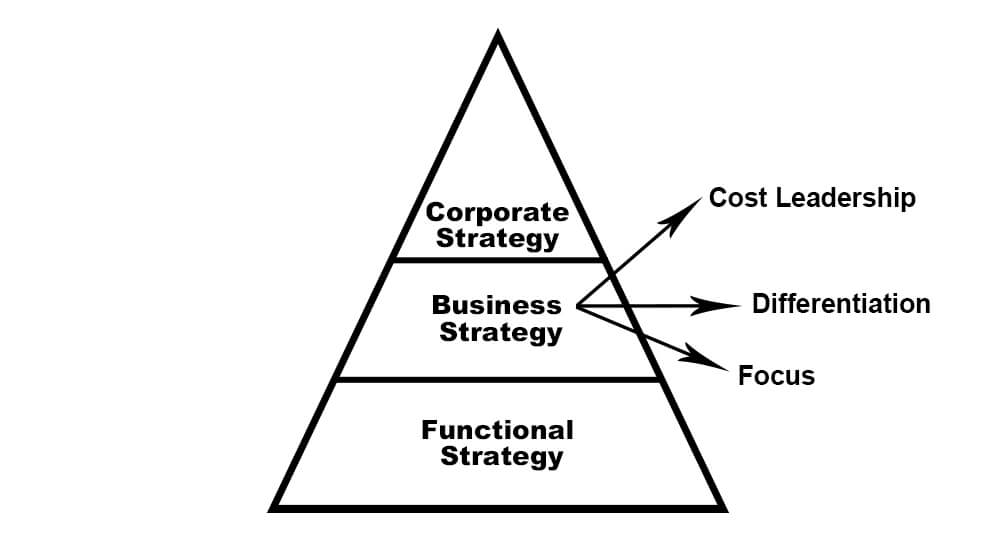
Business strategy is in the middle of the Porter pyramid, and today’s article will discuss this strategy in detail.
Types of Business Level Strategies
Porter grouped business strategies into three categories:
- Cost Leadership
- Differentiation
- Focus
#1. Cost Leadership
Cost is key to business.
All businesses compete for pricing, which determines profit margin. A low-priced product can attract a large audience but affect the profit margin, and a high-priced product serves fewer customers, but the profit margin will be high.
Product pricing is a key marketing parameter that helps businesses survive and stay ahead of the competition.
To lower the price, an organization can adopt the following practices:
- Use a simpler process
- Buy consumables in bulk to get the benefit of economy of scale
- Emphasize quality to lower the after-sales cost
- Use standard parts
- Train employees for better performance
An example of a cost leadership strategy is Amazon. Their profit margin is razor-thin, but they are profitable because of economies of scale. They attract large customers by offering products at a lower price.
#2. Differentiation
Being different is key to many businesses’ success. A business can position itself as a market leader through this strategy.
Apple’s products are known for high quality and price. Consumers buy them even though they are pricier than similar products. They care about being different and good quality. This approach supports quality over price.
However, this approach is not applied to price-conscious consumers, who do not buy the high-priced product when a similar lower-priced product is available.
Implementing this strategy is challenging, as developing a unique and different product is not easy.
Businesses study the market to find what competitors are missing and consumers’ requirements. Then they invest a lot of effort in ensuring their product fulfills customers’ requirements and includes features missed by the competitors. Also, the product must be of high quality.
An effective differentiation strategy can take a business to the next level, offering better customer satisfaction and higher profits.
Organizations can adopt integrated low-cost differentiation strategies or high-cost differentiation strategies.
An organization focuses on low-priced products to serve a bigger consumer base in a low-cost integrated strategy. Here, businesses focus on their core competencies, learn to produce products at a lower price, and keep the profit margin low.
Though they do not provide many value-added services, they instead focus on their core service and keep the customer happy. A combination of low price and being different help them cater to a larger market and achieve positive growth. An example of this strategy is budget airways.
High-cost differentiation strategies are adopted by larger businesses to serve a specific niche. This helps them provide the best service and earn premium profits.
#3. Focus
In this business-level strategy, organizations focus on a particular group of consumers and target them with special offers. Since the audience size is limited, organizations can offer a unique experience and serve them in the best possible way.
Usually, competition is not tough in this segment, but consumers are demanding and care about quality and reliability.
An example of this strategy is Rolls Royce. Their cars are costly and designed as per users’ requirements. No other car manufacturer does this.
They offer customers a unique experience and a high-quality product, and customers feel honored using the product.
Many organizations focus on low-cost products. They learn innovative ways to produce a product at a low cost and serve a particular niche.
They use many techniques such as economy of scale, simpler processes, standard parts, skilled employees, focus on quality, etc., to keep the product price low and customers happy.
Usually, small businesses adopt these strategies as they have fewer resources and cannot offer multiple products or serve a larger audience. This strategy requires better marketing and high product volume to benefit the economy of scale.
This business strategy is known as the Focused Low-Cost Strategy.
Summary
Businesses have three strategies – cost, differentiation, and focus – to use and compete with the market. Cost strategies focus on offering low price products to capture the market. Differentiation focuses on unique and different products and particular market segments. Focus targets a limited number of niche consumers.
Every business is unique, and organizations should select business strategies based on their competencies and the market conditions. Businesses do not require all strategies, so they should choose the best strategy to excel.
The goal must be to have a different high-quality product, an edge on the competition, serve the customer well, and earn profits.

Enjoyed reading the article. Thank you
U have not mentioned abut generic strategies by porter
Thank you