Communication is the process of delivering a message between two or more parties to create a shared understanding. It comes from the Latin word “communis,” which means to share. Communication can happen in many ways, such as speaking with someone, texting, or showing emotions like a smile or frown.
It is essential in everyday life and helps people share thoughts, ideas, and feelings. Effective communication ensures that the message is understood clearly by everyone involved.
Whether verbal or non-verbal, it connects people and allows them to work together, solve problems, and build relationships.
The Communication Process
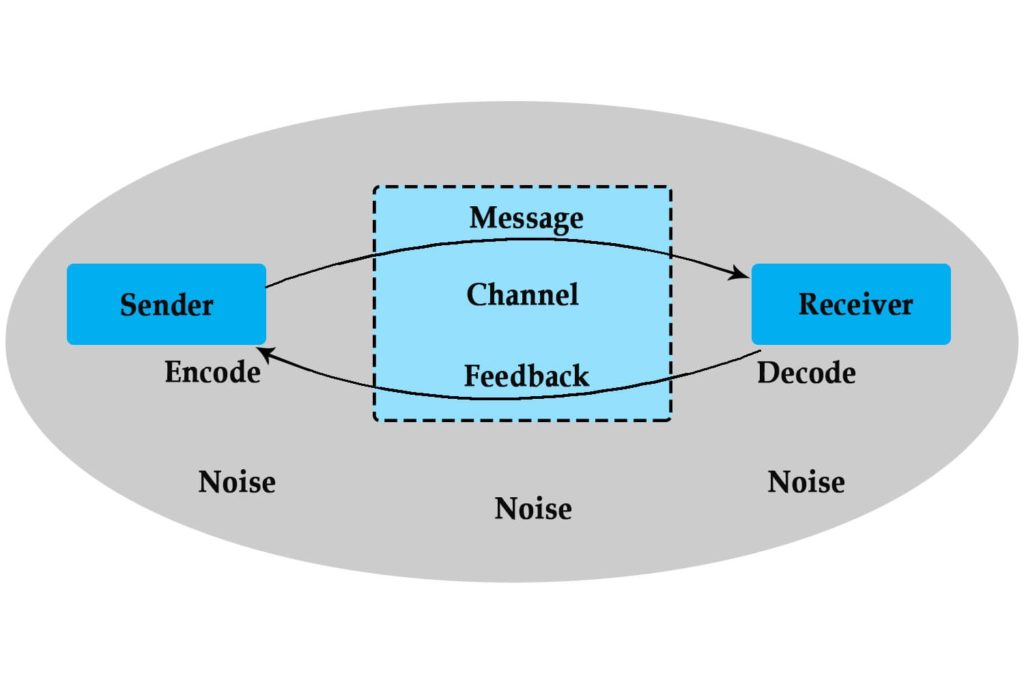
The communication process is a sequence where a sender transmits a message to a receiver through a channel. The receiver interprets the message and provides feedback to the sender, completing the cycle. Communication involves seven key elements, though some models simplify it to five: sender, transmission, noise, receiver, and feedback.
1. Sender
The sender is the originator of the message. They have an idea, thought, or concept to communicate. The sender plans the message, determines its purpose, and identifies the target audience. This step marks the beginning of the communication process.
2. Encoding
Encoding involves translating the sender’s thoughts into a message. This can include body language, written text, spoken words, or digital formats like video or audio. The sender must ensure the message is clear and appropriately formatted for the intended audience.
3. Message
The message is the information the sender wishes to convey. It can take various forms, such as spoken words, written text, gestures, or visual signals. The message represents the core idea being communicated.
4. Channel
The channel is the medium through which the message is transmitted. Examples include face-to-face conversations, emails, phone calls, or videos. Selecting the right channel is crucial for effective communication. Direct communication is ideal for formal discussions, while electronic channels work well for broad announcements.
5. Receiver
The receiver is the intended recipient of the message. They receive, process, and interpret the message in its transmitted form. The receiver’s understanding is vital for the communication process to succeed.
6. Decoding
Decoding is the process of interpreting the message into a meaningful form. This step ensures the message is understood as intended. Miscommunication occurs if the receiver fails to decode the message correctly, such as when it’s in an unfamiliar language.
7. Feedback
Feedback completes the communication process. It confirms that the receiver has received, decoded, and understood the message. Feedback can be verbal, non-verbal, or written. It allows the sender to evaluate the effectiveness of the communication and make improvements if needed.
Effective communication depends on clarity, selecting the right channel, and ensuring both sender and receiver mutually understand the message.
Barriers to the Communication Process
Noise is a significant barrier to effective communication. It can partially or completely disrupt the process, affecting how the message is transmitted, received, or interpreted. Noise can occur at any stage of communication, from encoding to feedback.
To minimize its impact, the sender should choose a channel with minimal interference and ensure clarity in the message.
Types of Noise in Communication:
- Faulty Text or Symbols: Misused or unclear language, symbols, or grammar in written communication can confuse the receiver.
- Incorrect Decoding: If the receiver misinterprets the message, the intended meaning is lost, leading to miscommunication.
- Poor Cell Connection: Interference during a call can distort audio, making it hard for the receiver to understand the message.
- Poor Call Quality: Low-quality audio can introduce misunderstandings, especially in critical discussions.
- Wrong Gesture: Misinterpreted body language or inappropriate gestures can send unintended signals, leading to confusion or offense.
Additional barriers can include:
- Physical Barriers: Environmental noise, such as machinery or background conversations, disrupts verbal communication.
- Cultural Barriers: Differences in language, beliefs, or customs that may hinder mutual understanding.
- Emotional Barriers: Stress, anger, or lack of trust can prevent clear communication.
- Technical Barriers: Malfunctioning equipment, such as faulty microphones or video conferencing tools interrupt communication.
Identifying and addressing these barriers is critical to ensure clear and effective communication.
Categories of Communication
Communication can be classified into various categories based on how it occurs, who is involved, and the methods used.
Here are the main categories:
- Verbal Communication: Verbal communication involves using spoken or written words to convey a message. It includes face-to-face conversations, phone calls, video conferences, emails, and text messages. This type of communication can be formal or informal, depending on the context and the relationship between the participants.
- Non-Verbal Communication: Non-verbal communication includes gestures, facial expressions, body language, posture, eye contact, and tone of voice. It conveys messages without words and often provides additional context or emotional cues to enhance verbal communication. It plays a significant role in how messages are interpreted.
- Written Communication: Written communication involves sending a message through written words. This can include letters, emails, reports, memos, and text messages. It allows for documentation, clarity, and formal communication and is often used in business or official contexts.
- Visual Communication: Visual communication uses visual elements like charts, graphs, images, logos, videos, and symbols to convey messages. It is often used in marketing, education, and media to support or enhance the verbal or written message.
- Mass Communication: Mass communication involves transmitting messages to a large audience through television, radio, newspapers, and the Internet. It is typically one-way communication from a sender to a large group of receivers and is often used for public announcements, advertisements, or entertainment.
Each category serves a different purpose, and selecting the right form of communication depends on the situation, the message, and the audience.
Key Communication Terms
Now, I will explain key terms used in the communication process:
Communication Channels
Communication channels are the methods used to send messages from one person to another. Examples include face-to-face conversations, phone calls, emails, and social media. The choice of channel depends on the message, urgency, and audience.
Encoding Messages
Encoding turns thoughts or ideas into a message that the receiver can understand. The sender decides how to express the message using words, body language, or images. This step ensures the message is clear and easy to transmit.
Decoding Messages
Decoding is when the receiver interprets or understands the message sent by the sender. The receiver translates the message from its form (like text, voice, or gestures) into meaning. Effective decoding depends on the receiver’s knowledge and understanding of the message.
Feedback
Feedback is the response or reaction the receiver gives after receiving the message. It helps the sender know whether the message was understood. Feedback can be verbal, non-verbal, or written, ensuring successful communication.
Summary
Effective communication is essential for ensuring that messages are delivered, received, and understood. A robust communication process minimizes misunderstandings and ensures that the sender and receiver are aligned in their understanding. Crafting the message carefully and selecting the right medium is crucial to avoid barriers or noise that can disrupt the process.
By addressing potential obstacles and ensuring clarity at each step, communication can become a powerful tool for successful interactions, whether in personal or professional relationships. Well-executed communication leads to better collaboration, decision-making, and problem-solving.

Hi Parsadi.
I now understand what communication process is all about. Effective communication meets beyond bullying, i think we can add in a noise phone call cuts. This can be in a form of poor networking or personal decisive when sender is ready to delver his or her message. For example, someone had planned to deliver a message to friend,in a due cause a friend says let me call you back while you may be you have just started delivering your message to retain to what you started sometimes becomes transmitting the message causing communication breakdown.
But very impressive to learn all the nonverbal cues, the bullying happens in all social media platforms and the time that individual can spend to deliver his or her message to audience or receiver. Impressed to know such amazing barriers to communication processes such us language, tones, and many more.