The critical path method and critical chain method represent schedule network diagramming techniques used in developing the project schedule.
This post will discuss the difference between these two diagramming techniques, i.e. critical path vs critical chain method.
The critical path method is the oldest technique, while the critical chain method is a relatively new and modified version of the critical path method.
Critical Path
A network diagram consists of many paths with several activities connected by different relationships. Of all these paths, the longest path is known as the critical path, and the duration of the critical path is the duration of the project.
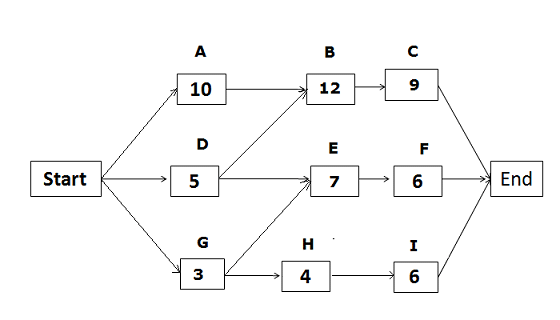
In the above network diagram, the path “Start-A-B-C-End” is critical as it has the longest duration.
All activities on a critical path are known as critical activities, and any delay in completing these activities will delay the project by the same amount of time.
How to Draw a Critical Path Diagram
To draw a network diagram, you will find all the activities for your project. Then you have to sequence them and determine the duration of each activity and the relationships among them.
Now you will draw the network diagram and find the paths’ duration. From there, you can identify the critical path.
Types of Float in Critical Path
The critical path has two types of float:
- Total Float
- Free Float
The Total Float is the time an activity can be delayed without delaying the overall schedule. The total float is zero on a critical path.
The Free Float is the amount of time an activity can be delayed without delaying the early start of its successor activity.
From a PMP exam point of view, the critical path concept is very important. You will see many questions in the exam on this subject. You may need to draw a network diagram and find a critical path, the duration of paths, early start, early finish, etc.
Critical Chain
The network diagram with a critical path has some inherent drawbacks, such as:
- Any delay in any critical activity will delay the project.
- It assumes an unlimited supply of resources.
- The chances of completing the project within the schedule are low.
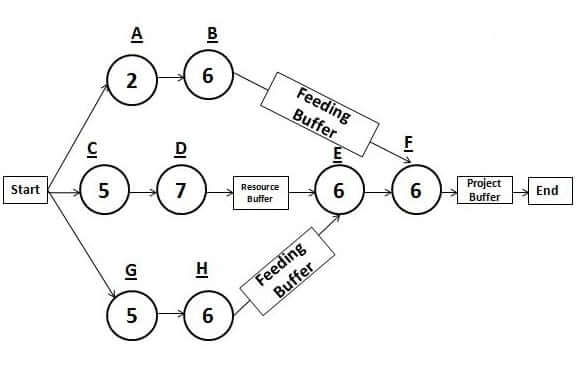
Moreover, since the duration of the critical path is the duration of the project, project managers tend to inflate the duration of activities on a critical path to keep an extra margin for completing the project.
These miscalculations affect the schedule.
Therefore, the critical path method was upgraded to remove these drawbacks and named the critical chain method.
In the critical chain method, the critical path is optimized based on resource availability, which increases the chances of completing the project in the estimated time. However, including resource availability increases the duration of the project.
Please note that you will not find the term critical chain in the sixth edition of the PMBOK Guide. However, you may find a question based on this technique, as this is a schedule network diagram technique.
In the critical chain method, instead of the term “float,” the term “buffer” is used. There are three types of buffers:
- Project Buffer
- Feeding Buffer
- Resource Buffer
The Project Buffer is added at the end of the project. Any activities which are delayed will eat up this buffer.
The Feeding Buffer is added to the non-critical chain, so any delayed activities will use the feeding buffer.
The Resource Buffer is a resource that is kept alongside the critical chain to ensure the continuity of the work.
For the PMP exam, it is sufficient to know that the critical chain method is a resource-optimized diagram and uses buffers. You will not need to draw any CCM diagrams in the exam; you must know these theoretical concepts.
Remember that the critical chain is an updated version of the critical path where you consider the availability of resources and their optimization. This, of course, can lead to a different, more realistic critical chain.
In a critical chain diagram, you will have many chains but only one critical chain.
Differences between Float and Buffer
There are many differences between the float and the buffer. Floats are used in the critical path method, and buffers are used in the critical chain method.
- The float is calculated as the difference between the critical and non-critical path, while the buffer is based on contingencies.
- On the critical path, the float is zero, while the buffer is not zero in the critical chain.
- The float cannot be used to check the project status, while buffers can be used to analyze the project status.
- A float can be either a total or a free float, while a buffer can be a feeding buffer, a project buffer, or a resource buffer.
- In the critical path, activities can have an early start or late start, early finish, or late finish, whereas, in the critical chain, activities have only a start and an end.
Differences Between Critical Path and Critical Chain Method
There are many differences between the critical path and the critical chain method. The critical path is about managing activity, while the critical chain is about managing buffers.
Resources
The critical path method assumes that all resources will be provided whenever needed. On the other hand, the critical chain method considers resource availability as limited and builds a realistic schedule based on the resources at hand. Though this process increases the schedule duration, it provides a better, more realistic schedule.
Float/Buffer
In the critical path method, it is not useful to gain time by completing an activity earlier as the next activity cannot be started before its early start time. So you cannot utilize the time by completing a previous activity early. However, if there is a delay in any activity, the next activity will be delayed.
This is not the case with the critical chain. When an activity is completed, you can start the next activity, and the time gained will be added to the project buffer.
Misuse of Float
In the critical path method, if an activity has a float, the team member will not start the activity till its late start and utilize the float.
Again, in the critical path, you can add the delay but cannot add the gain. Also, if an activity has extra time, the work will expand to fill all available time. Sometimes this phenomenon is known as the Student’s Syndrome.
This is not the case with the critical chain, as the buffer is placed at the end of the project, and each activity has its real-time duration.
Summary
A critical path is essential for developing a project schedule network diagram; however, this method has some drawbacks, so the critical chain method was developed. The critical chain method is optimized for resource availability, and the developed schedule is more robust and reliable. These days, the critical chain method is more popular than the critical path method; however, the term critical path is still more popular than the critical chain and is often used as a synonym for the critical chain.
Do you use a critical chain-based schedule in your projects? If yes, please share your experiences in the comments section.
Well written!
I am using Critical Chain Method in my projects. But it is so hard to accepted it to clients because of they are familiar with Critical Path Method. The article is explained very clearly differences and advantages!