Every entrepreneur dreams of watching their company grow. Yet growth does not happen by accident. A growth strategy is a deliberate plan for expanding a business’s revenue, customer base, or product offerings. It is a roadmap that sets clear goals and outlines how to reach them.
In today’s digital world, video has become a dominant tool—91% of businesses use video marketing and 93% of marketers say it is an important part of their overall strategy. At the same time, economic pressures remain; recent surveys show only about 43% of small businesses feel their local economy is in good health and inflation is still their top challenge. These trends underline why a thoughtful growth plan is essential.
In this guide you will learn what a growth strategy is, why it matters, and how to craft one. We will explore proven frameworks like the Ansoff Matrix, walk through the steps of planning, and look at real‑world examples.
What is a Growth Strategy?
A growth strategy is a structured plan that helps a business expand its reach, revenue, or products. It is more than a marketing campaign; it looks at the company’s goals, resources, market conditions, and risk tolerance.
A good strategy identifies where to focus (new markets, new products, or deeper penetration of existing ones) and details how to get there. Without a clear strategy, growth efforts can be scattered and ineffective. With one, teams work toward shared objectives and measure progress along the way.
Why Growth Strategy Matters
The business landscape has changed dramatically over the past few years. Digital media, artificial intelligence and changing consumer expectations create both opportunities and challenges. Most marketers now consider video crucial to their plans, while small businesses face headwinds such as inflation and talent shortages.
A well‑crafted growth strategy helps you respond to these shifts. It allows companies to allocate resources wisely, stay agile and build resilience. It also signals to investors and employees that leaders have a clear plan for the future.
Types of Growth Strategies
Business often starts with the Ansoff Matrix, a tool that helps leaders weigh the risks and rewards of different growth paths. Igor Ansoff introduced this matrix in 1957; it organizes choices around products and markets.
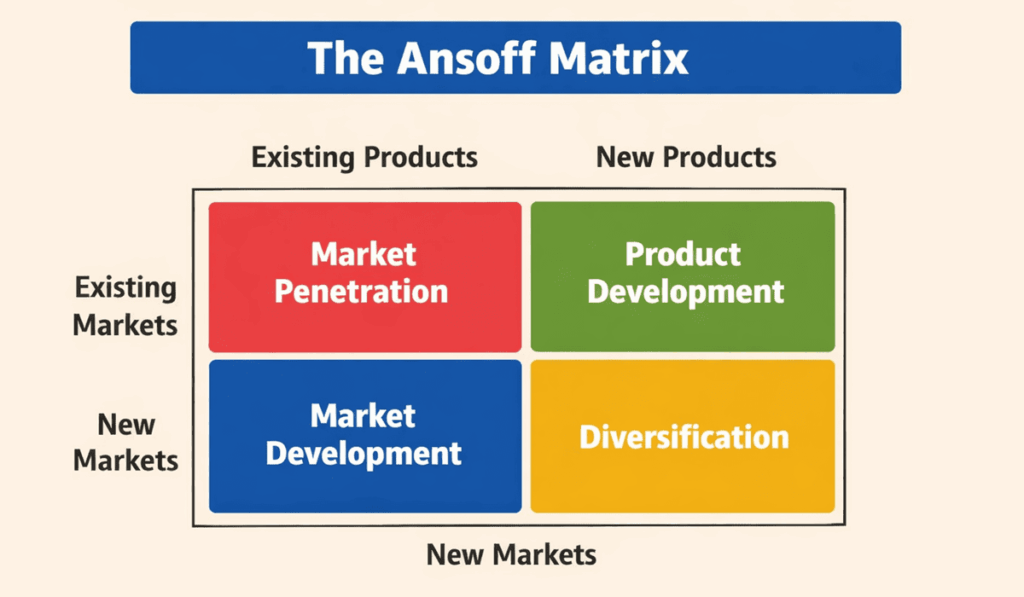
The four strategies are:
- Market Penetration: Selling more existing products in your current market. This is the least risky approach because you know both the product and the customers. Tactics include offering discounts, bundling products, improving customer service and increasing marketing spend.
- Market Development: Introducing existing products to new markets, such as new regions or customer segments. This strategy leverages what you already know but requires building awareness in a new audience.
- Product Development: Creating new products for your existing market. This approach builds on established customer relationships and brand loyalty. It may involve research and development, licensing another firm’s technology, or partnering with manufacturers.
- Diversification: Launching new products in new markets. This is the riskiest option because it combines product development and market development. Diversification can be related (where synergies exist) or unrelated (where the new business is completely different), and it can bring high rewards when done well.
Growth Strategy Frameworks
Growth strategies are easier to design when you use structured frameworks. Below are three popular models that help you analyze choices and risks.
1. The Ansoff Matrix
As described above, the Ansoff Matrix clarifies whether you are targeting new or existing products and markets. It encourages leaders to consider risk. Market penetration is generally safest, while diversification carries the highest risk. Use this framework to decide if you should sell more of what you already offer, expand into new regions, develop new products, or branch into entirely new industries.
2. BCG Growth‑Share Matrix
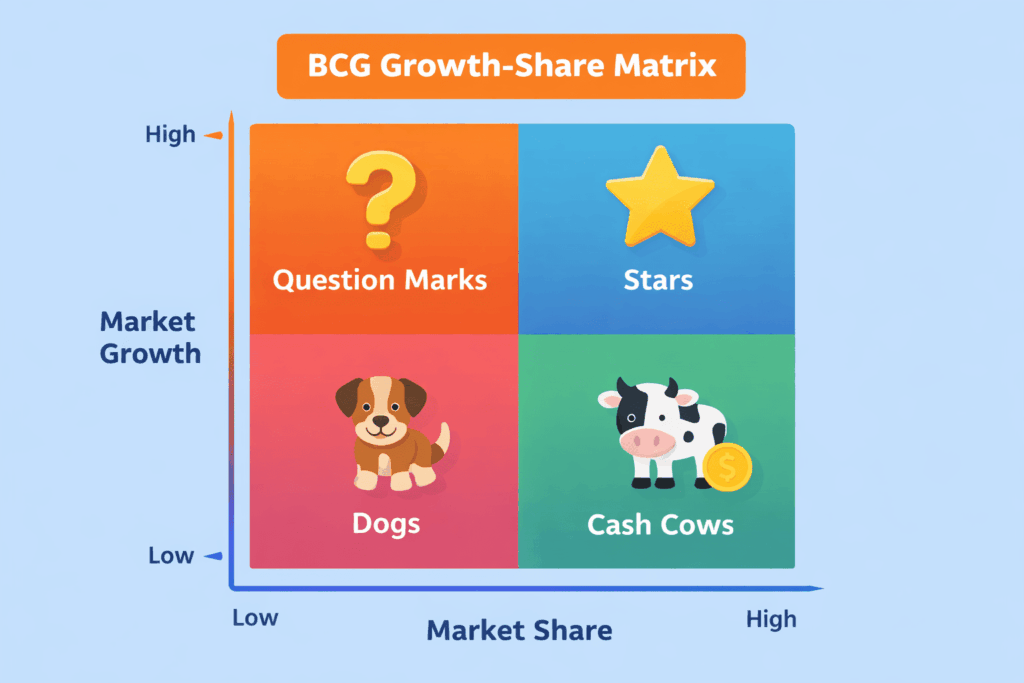
Developed by the Boston Consulting Group, this matrix categorizes products into four quadrants based on market growth and relative market share: Cash Cows, Stars, Question Marks and Dogs. Cash Cows have high market share but low growth; companies “milk” them for cash to fund growth elsewhere. Stars have high share and high growth; they deserve investment.
Question Marks have high growth but low share; leaders must decide whether to invest or divest. Dogs have low share and low growth; they may be candidates for liquidation or repositioning. Use the BCG matrix to allocate resources across your product portfolio and avoid spreading efforts too thin.
3. Porter’s Five Forces
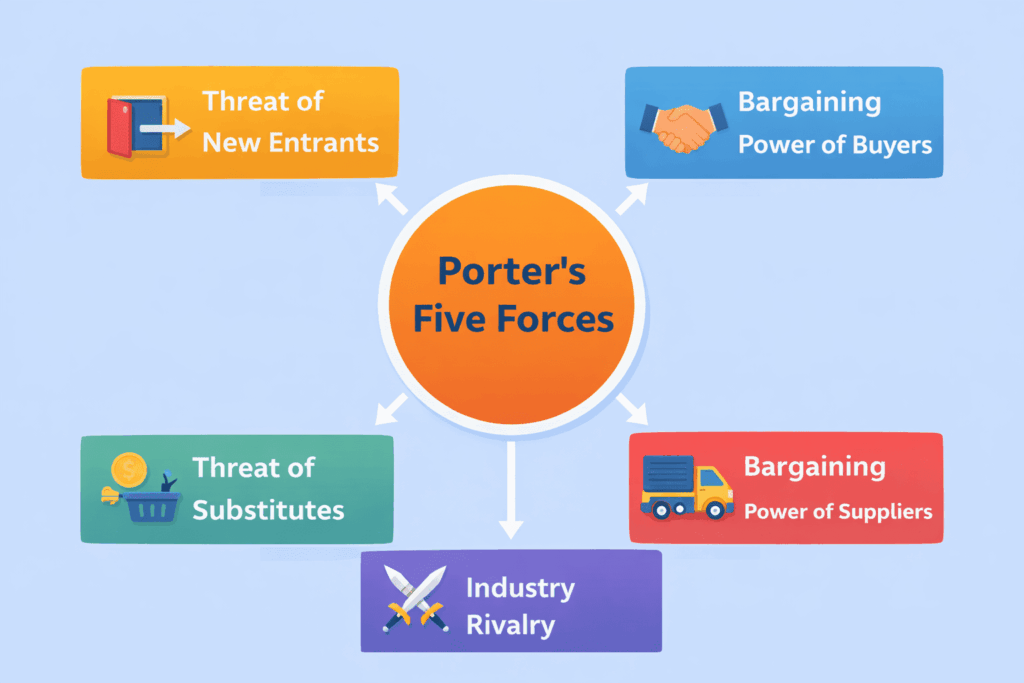
Michael Porter’s Five Forces model examines the competitive forces in an industry: rivalry among competitors, bargaining power of suppliers, bargaining power of buyers, threat of substitutes, and threat of new entrants. Analyzing these forces helps determine which markets are attractive for expansion and where margins may be squeezed. For example, entering a market with many substitutes and powerful suppliers may require a differentiated strategy.
4. Strategy Diamond
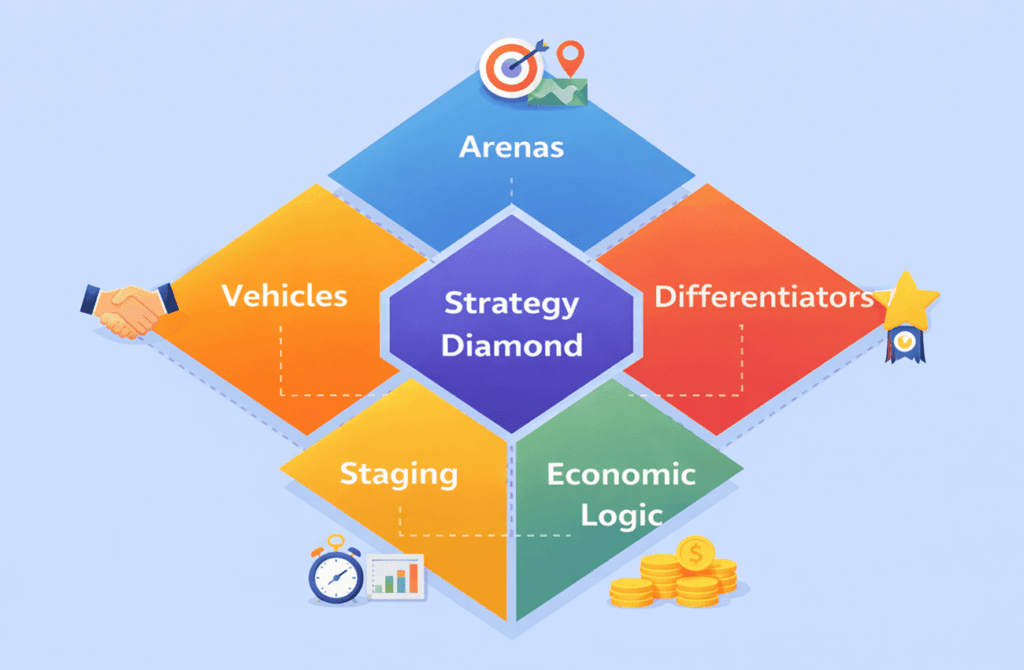
Developed by Donald Hambrick and James Fredrickson, the Strategy Diamond looks at five elements: Arenas (where the business will compete), Vehicles (how it will get there—e.g., organic growth, partnerships), Differentiators (what makes it unique), Staging (the speed and sequence of moves), and Economic Logic (how the company will make money). This holistic view ensures that growth plans align with the company’s mission and capabilities.
Step‑by‑Step Growth Planning
Creating a growth strategy involves more than choosing a framework.
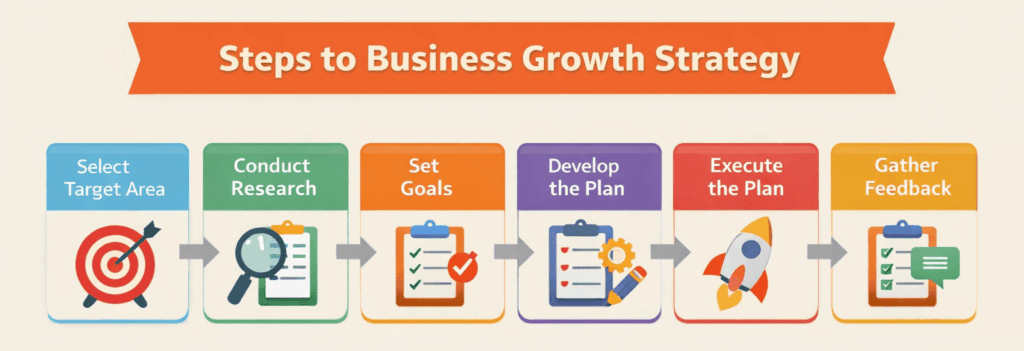
Follow these six steps to craft a plan that works.
1. Choose a Growth Area
Decide where you want to grow. Are you looking to enter a new market, increase sales in a current segment, launch a new product line, or acquire a competitor? Think about your company’s strengths and resources. A focused growth area keeps efforts aligned and helps you avoid spreading resources too thin.
2. Conduct Market Research
Market research provides the data needed to make informed choices. Survey potential customers, analyze competitors, study economic trends and seek feedback from industry experts. For instance, if most customers prefer buying online, investing in an e‑commerce platform may be more profitable than opening new physical stores.
3. Set Clear Goals
Set measurable targets such as increasing revenue by 15% in one year, opening in three new countries, or launching two new products. Goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time‑bound (SMART). Align them with your long‑term vision and mission.
4. Develop the Plan
With research and goals in place, create a detailed action plan. Outline the budget, timeline, marketing tactics and responsibilities. Include plans for hiring, technology investment and partnerships. A written plan keeps everyone on the same page.
5. Execute the Plan
Execution turns ideas into results. Launch your campaigns, start production, enter new markets and monitor progress. Communicate clearly with your team and stakeholders. Adapt quickly if challenges arise. Stay committed, but remain flexible.
6. Collect Feedback and Adjust
Gather feedback from customers, employees and partners. Use key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress. If results fall short, adjust your strategy. Continuous improvement makes your growth plan resilient. Many businesses iterate their strategy over time to stay aligned with market realities.
Growth Strategy Examples
Examining how well‑known companies grow can inspire your own plan.
Facebook (Meta)
Facebook started as a social network for Harvard students in 2004. Instead of opening its platform to everyone immediately, the company used a market penetration strategy: it focused on a narrow user base and perfected its product. Later, it opened to other colleges, then high schools, and finally to the public. This staged approach allowed the company to gather feedback, improve the user experience and build a loyal community before scaling worldwide.
Amazon
Amazon launched in 1995 as an online bookstore. By offering a vast selection, easy navigation and user reviews, it provided a superior customer experience. After gaining a strong foothold, the company pursued a diversification strategy, adding music, electronics, cloud services and media streaming. Amazon leveraged its logistics network and customer data to expand into new categories and markets. The result is one of the world’s largest and most diverse online retailers.
Netflix
Netflix offers another lesson in strategic evolution. It began in 1997 as a DVD rental company. By 2007 it adopted a product development strategy, launching its streaming service to meet growing demand for on‑demand entertainment. Netflix then invested heavily in original content, differentiating itself from competitors and reducing reliance on licensed shows. Today, its global presence is a result of careful market development and a willingness to disrupt its own model.
Local Artisan Bakery Example
Not all growth stories involve tech giants. Imagine a small bakery in Kuwait that sells bread and pastries. To grow, the owner could follow a market development strategy by offering delivery service to nearby neighborhoods or selling products at local markets. Alternatively, a product development strategy might involve adding gluten‑free or keto options to attract new customers. By researching customer preferences and adjusting offerings, even a small business can expand sustainably.
Emerging Growth Trends
Modern growth strategies are shaped by technological and societal shifts. Here are a few trends to consider:
- Video and Digital Content: Most businesses incorporate video in their marketing and nearly all video marketers view it as essential. Short‑form videos, live streams and tutorials help brands reach wider audiences and build trust.
- Data‑Driven Decisions: Big data and AI make it easier to understand customer behavior. Businesses that analyze data to personalize products and optimize pricing tend to outperform those that rely on intuition alone.
- Sustainability: Consumers increasingly prefer brands that reduce waste and support ethical practices. A sustainability strategy can open new markets and enhance brand loyalty.
- Remote and Hybrid Work: Companies that embrace flexible work arrangements can access global talent, reduce overhead and respond quickly to market changes.
- Community Building: Cultivating a community around your brand—through social media groups, forums or events—creates loyal customers who become advocates.
FAQs
Q1. What is a growth strategy and why do I need one?
A growth strategy is a plan to expand your business by targeting new markets, products or customers. Without one, growth efforts can be wasteful and directionless.
Q2. How long does it take to see results?
The timeline varies. Some tactics, like online promotions, yield quick feedback; others, like entering a new market, may take years. Set milestones and review progress regularly.
Q3. Do I need a large budget to grow my business?
Not necessarily. Many growth tactics—such as social media marketing, partnerships and customer referrals—cost little. Start with what you have and reinvest profits into further growth.
Q4. How do I measure success?
Use metrics aligned with your goals, such as revenue growth, customer acquisition cost, retention rate or product adoption. Regularly review data and adjust your approach.
Conclusion
A growth strategy provides direction and discipline in a fast‑changing world. By understanding frameworks like the Ansoff Matrix, setting clear goals and adapting to trends such as video marketing and economic shifts, companies can build resilience and seize new opportunities. Start by choosing a growth area, conducting research and writing down your plan. Then execute, learn and refine. Growth may be challenging, but with a thoughtful strategy it becomes a purposeful journey.
