You must consider several internal factors to develop a constructive work environment in your organization. These factors influence how employees work, behave, and interact with one another. Understanding them is crucial for creating a positive and productive workplace culture. Internal factors such as leadership style, employee motivation, company values, and communication processes play a key role.
When managed well, these elements can improve teamwork and performance. Ignoring them may result in conflicts and reduced efficiency.
In today’s blog post, I will explain the internal factors that can affect organizational culture in detail.
What is an Internal Environment?
The internal environment of an organization is the conditions that shape its atmosphere and influence employee behavior. It defines the relationships among employees, managers, and leadership and the organization’s culture, processes, and procedures.
In a traditional internal environment, employees follow managerial instructions with limited interaction beyond formal orders. Managers maintain a strict and authoritative role, and communication is primarily directive.
In contrast, modern organizations emphasize a more collaborative approach. Managers engage with employees, provide guidance, and support career development. This develops a healthier work environment where employees are encouraged to grow and perform at their best.
7 Components of the Internal Environment of an Organization
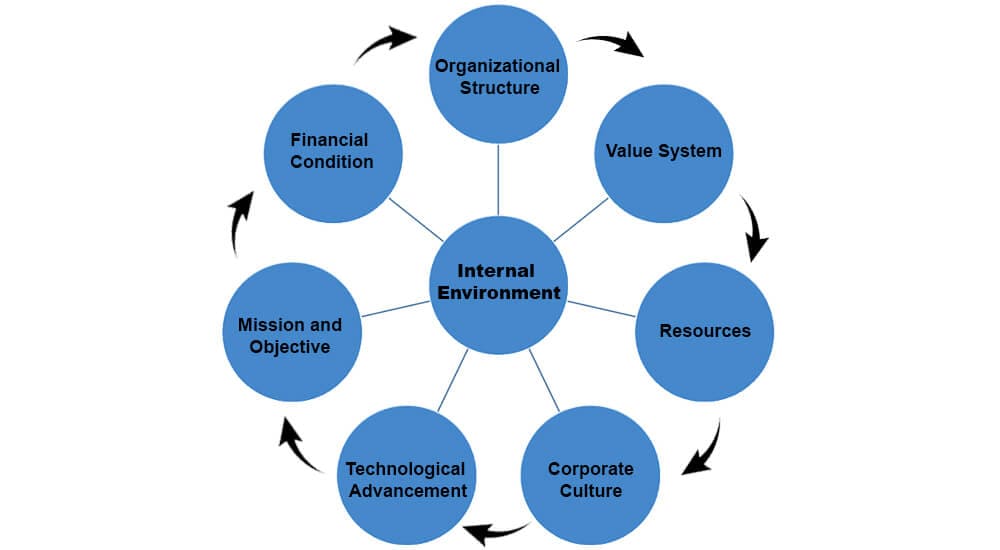
The following are the 7 factors that can affect the internal environment of any organization:
1. Organizational Structure
The organizational structure is the system that defines how activities are organized and who reports to whom. It creates a framework for decision-making and operations.
There are three main types of organizational structures:
- Projectized: In a projectized structure, teams are built around projects, which creates a fast-paced and flexible work environment
- Matrix: Employees report to multiple managers in a matrix structure, promoting a balanced approach and collaboration.
- Functional: A functional structure divides the organization into departments based on expertise, creating a more stable and predictable environment.
The structure of an organization directly affects communication, workflow, and employee behavior. A rigid structure might limit creativity, while a flexible one encourages innovation and adaptability.
For example, projectized organizations thrive on quick decisions, while functional organizations excel in long-term planning. Understanding the organizational structure is essential to improving productivity and building strong workplace relationships.
2. Value Stream
The value stream represents an organization’s principles, policies, and procedures. It defines how the organization treats its employees and customers. Organizational norms, like work ethics and company standards, are also part of the value stream. These norms ensure consistency and set expectations for performance and behavior.
Employees are expected to work within their organization’s value system. If an organization prioritizes customer satisfaction, employees will focus on delivering excellent service. If the value system emphasizes teamwork, employees will collaborate to achieve goals. A strong value stream leads to an organized, disciplined, and productive work environment.
On the other hand, weak or unclear policies can create confusion and reduce efficiency. Organizations with a well-defined value stream promote fairness, accountability, and a positive culture, which improves employee satisfaction and customer trust.
3. Resources
Resources are critical for any organization to function effectively. These include human resources, equipment, technology, workspaces, consumables, and infrastructure. Employees are the most important resource, as they drive productivity and innovation. An organization with skilled, motivated employees can achieve its goals efficiently.
Resources determine the organization’s competitive advantage. For example, a company with advanced equipment and better infrastructure can outperform competitors. Similarly, well-maintained workspaces and tools help employees perform better and stay motivated.
Disorganized or insufficient resources can harm the internal environment. Employees may face frustration due to a lack of tools, poor facilities, or limited staff. Organizations that invest in training employees, upgrading equipment, and improving infrastructure create a supportive environment where employees can thrive. Well-managed resources lead to higher job satisfaction, reduced turnover, and better performance.
4. Corporate Culture
Corporate or organizational culture refers to the values, beliefs, and practices that shape employee behavior. It influences how employees interact with each other and the outside world. A positive corporate culture creates a strong foundation for the organization’s success. It affects communication, decision-making, and daily operations.
In organizations with a supportive culture, employees feel valued and motivated. For example, companies prioritizing open communication and teamwork develop trust and collaboration. On the other hand, a rigid and bureaucratic culture can create barriers and reduce morale. Employees in such environments may feel less involved and disengaged.
A strong corporate culture also improves the organization’s reputation. It attracts talented individuals who align with the company’s values. A healthy culture increases employee retention, boosts productivity, and encourages innovation. Organizations that build a positive culture create long-term success and competitive advantages.
5. Technological Advancement
Technological advancement significantly impacts an organization’s internal environment. Modern technology makes work faster, more efficient, and less stressful for employees. It allows organizations to automate tasks, improve communication, and simplify operations. Employees in technologically advanced organizations can focus on important tasks instead of repetitive manual work.
For example, project management software, communication platforms, and advanced machinery save time and enhance productivity. Technology also enables remote work, which gives employees flexibility and improves work-life balance.
Organizations adopting new technologies gain a competitive edge over those that do not. However, organizations that fail to update their technology may experience reduced productivity and employee dissatisfaction. Staying current with technological advancements helps organizations remain efficient, adapt to changes, and create a positive internal environment.
6. Mission & Objectives
An organization’s mission and objectives provide direction and purpose. The mission statement explains the organization’s reason for existence, while the objectives outline specific goals the organization wants to achieve. Together, they influence how tasks are assigned, and the reporting system works.
Employees work more effectively when they understand the organization’s mission and objectives. For example, employees prioritize providing excellent service if the mission focuses on customer satisfaction. Clear objectives help employees align their work with the organization’s goals.
A lack of clear mission and objectives can create confusion and reduce productivity. Employees may feel uncertain about their roles or the organization’s priorities. On the other hand, a clear mission and well-defined objectives build motivation, teamwork, and focus. Organizations with strong goals give employees a sense of purpose, creating a more positive and driven work environment.
7. Financial Conditions
An organization’s financial condition directly affects its internal environment. A strong financial position allows the organization to invest in growth opportunities, technology, and employee development. It also creates a sense of stability and security for employees, which boosts morale and motivation.
Organizations with healthy finances can offer their employees better salaries, incentives, and facilities. This improves job satisfaction and attracts talented professionals. Financial strength also enables organizations to expand operations, take risks, and innovate.
In contrast, organizations with limited financial resources face several challenges. Budget constraints may lead to delays in hiring, poor infrastructure, or fewer growth opportunities for employees. Financial struggles can create uncertainty and stress, which negatively impacts employee performance.
Maintaining a strong financial position is essential for organizational success. It ensures a productive internal environment where employees feel secure, supported, and motivated to contribute to the organization’s growth.
Summary
The internal environment is critical in determining an organization’s efficiency and success. Internal factors and workplace dynamics shape performance and productivity by directly influencing employees’ behavior and decision-making. A positive and healthy internal environment is essential to motivate employees and develop a culture of engagement and excellence.
Employees who feel supported and valued are more likely to contribute effectively to the organization’s goals. Therefore, organizations must proactively address internal challenges, nurture strong internal systems, and create an environment conducive to growth and sustained success.
