International marketing is the marketing of products or services across borders. It is also called global marketing. It helps businesses reach different countries with different cultures. Companies use localized approaches to adapt to the unique needs of each market. This may include changes in packaging, pricing, or advertising.
The goal of international marketing is to build strong connections with customers worldwide. It allows businesses to grow by reaching larger audiences. International marketing involves understanding laws, languages, and traditions in other countries.
By respecting cultural differences, businesses can create trust and loyalty. It is a key strategy for global business success.
Importance of International Marketing
International marketing is important because it helps businesses grow and reach new customers worldwide. It allows companies to expand beyond their local markets and increase profits.
By entering global markets, businesses can reduce dependence on one country’s economy. It also helps create brand awareness across different regions. International marketing encourages innovation as companies adapt to different cultures and preferences. It supports better understanding and respect for diverse cultures.
This builds trust and long-term customer relationships. Additionally, international marketing strengthens a company’s competitive edge by helping it stay relevant in a globalized world.
Examples of International Marketing
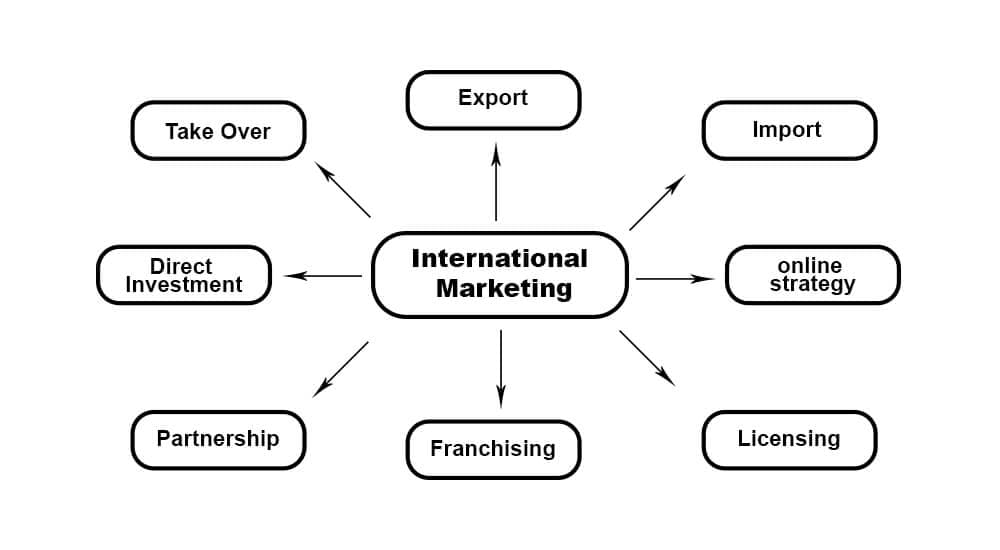
Export
Exporting is a traditional and common form of international marketing. It involves businesses shipping products to other countries. Exports can be direct or indirect. In indirect exports, companies use distributors or agents to reach buyers. Direct exports mean businesses directly market their products internationally through local units, direct shipments, or local agents. This method poses low risks as it does not influence the political landscape of foreign markets.
Import
Importing is the opposite of exporting. Importers purchase products from other countries and sell them locally. In this case, the exporter has minimal responsibility, as the importer manages legal liabilities in their home country. An import to one nation is an export from another, facilitating trade across borders.
Online Strategy
Online strategies are increasingly popular for global marketing. Businesses do not need a physical presence in foreign countries. They create websites to accept orders from anywhere. Orders are processed and shipped from the company’s warehouse, offering a simple, cost-effective global approach without the complexities of traditional international marketing.
Licensing
Licensing allows a business to grant third parties the right to use its intellectual property for a set period in exchange for royalties. This can involve patents, trade names, or production processes. It is commonly used in manufacturing and allows businesses to earn revenue by leveraging their intellectual property without significant investments in foreign markets.
Franchising
A company licenses local businesses to operate under its brand and standards in franchising. The local unit runs the operations, while the parent company provides ongoing support. Franchising is often used in service industries, like restaurants or hotels, where quality control is important and local units must follow strict company guidelines.
Partnership
Two companies collaborate to market and sell products in a partnership or joint venture. Both parties share responsibility and risk. This strategy allows businesses to combine their strengths to gain market share and operate in foreign markets. Partnerships work well because both companies contribute their unique capabilities, benefiting from shared expertise and resources.
Direct Investment
Direct investment involves a business setting up operations in a foreign country. This strategy requires substantial financial investment and an understanding of local laws and regulations. Direct investment gives companies full control over their operations but involves greater risk than other international marketing methods.
Takeover
A takeover occurs when a business acquires a controlling stake or fully buys a local company. The acquiring company then reshapes operations as per its requirements. This method, typically used by larger businesses, allows them to quickly gain market share, technology, and local expertise, often modifying operations for increased efficiency and growth.
Benefits of International Marketing
The following are a few benefits of international marketing:
- Market Expansion: Businesses can reach new customers and enter untapped markets.
- Increased Revenue: Expanding into global markets can increase sales and profits.
- Reduced Risk: Businesses can offset any market’s downturns by operating in multiple countries.
- Brand Recognition: International marketing helps build a strong, global brand identity.
- Diversification: It allows companies to offer their products to various cultures and markets, reducing dependency on one economy.
- Economies of Scale: Businesses can produce goods in larger volumes, lowering costs and improving efficiency.
- Innovation: Exposure to different markets leads to new ideas, improved products, and competitive advantage.
- Cultural Exchange: It encourages learning and respect for other cultures, strengthening global relationships.
Summary
International marketing involves businesses in two or more countries and helps exchange products or services across borders to meet the consumers’ requirements. It helps businesses use their surplus production and grow their sales and brand recognition while increasing their responsibility. With global marketing, businesses must handle local customs, laws, regulations, etc.
