An organization is a group of people working together to achieve a shared goal. Its structure assigns tasks and responsibilities to its members, helping divide work and ensuring each person contributes to the organization’s objectives.
Organizations can be formal, like businesses and schools, or informal, like clubs or groups of friends. Sometimes, people create organizations for temporary goals, like planning an event. These temporary groups may grow into long-lasting structures if the need continues.
An organization efficiently aligns efforts and resources toward a common aim. Whether big or small, an organization helps people achieve more together than they could individually. It relies on cooperation, communication, and shared understanding among its members.
Purpose of an Organization
An organization exists to fulfill a purpose, guided by its mission, vision, values, and priorities. These elements shape its goals and operations.
- Mission: The mission defines the organization’s purpose and the reason for its existence. It unites people to work towards a common goal. The mission may be formal, like a business plan, or informal, such as a shared understanding within a group.
- Vision: The vision describes the organization’s desired future outcome. It inspires and motivates people by presenting a clear image of success.
- Values: Values are the principles and beliefs that guide how the organization achieves its goals. They influence decision-making and behavior within the group.
- Priorities: Priorities focus on what is most important to achieve the organization’s objectives. They adapt to changing circumstances but must align with the mission, vision, and values.
Characteristics of an Organization
An organization has specific characteristics that make it work effectively. These features ensure smooth operations and help achieve goals.
- Defined Structures: Every organization has a clear structure. It shows how tasks and teams are arranged to work together.
- Clear Roles and Responsibilities: In an organization, everyone knows their job. This clarity helps people focus on their tasks without confusion.
- Specialization: Organizational employees often focus on specific tasks, which allows them to become experts in their roles.
- Division of Employees: Employees are grouped based on their skills and tasks. This division ensures that work is done efficiently.
- Flexibility: A good organization can adapt to changes. It adjusts its processes to meet new challenges or opportunities.
Types of Organization Structures
#1. Organic Organizational Structure
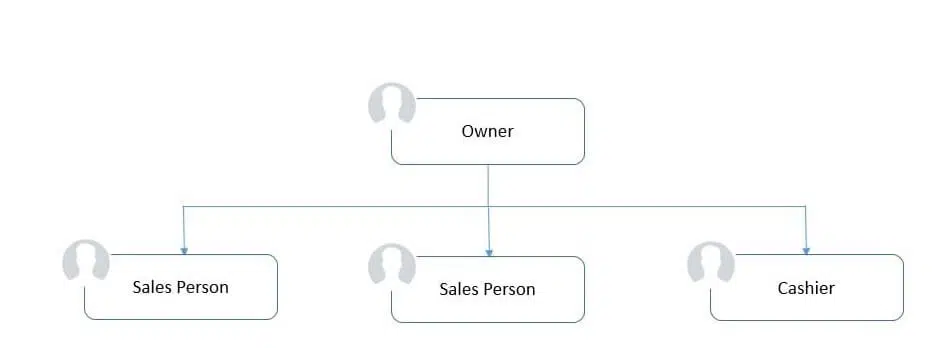
An organic organizational structure is simple and flexible. It often involves a single owner working alone or with one or two employees. The owner directly manages and collaborates with staff. This structure is common for freelancers, solopreneurs, and One-Person Companies (OPCs), making it ideal for small-scale, personalized operations.
#2. Functional Organizational Structure
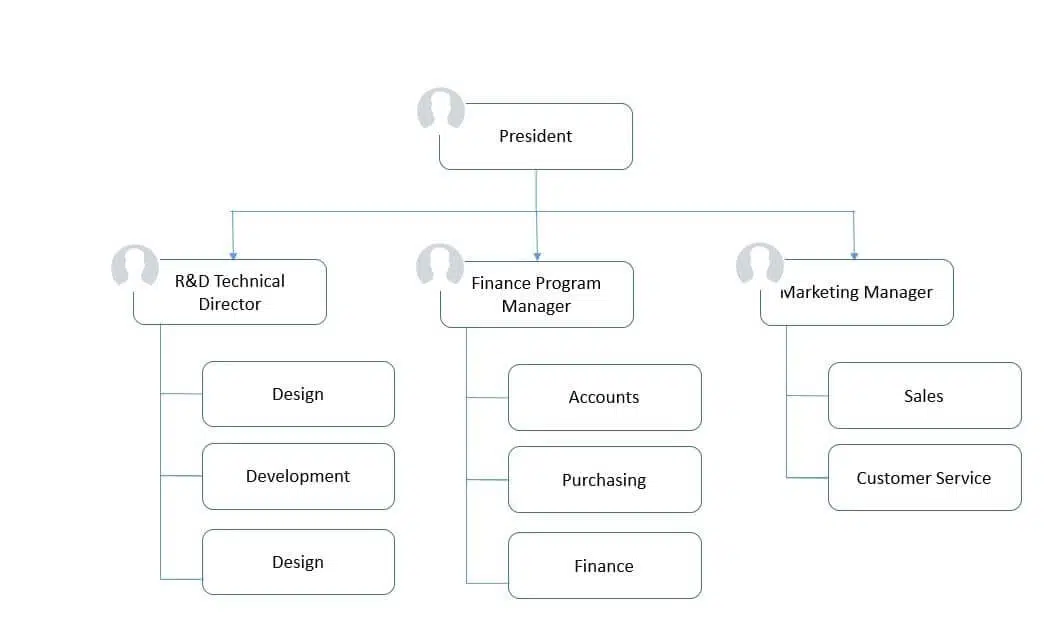
A functional organizational structure divides an organization into departments based on specific skills or functions, such as finance, sales, and marketing. Each group focuses on its expertise, promoting efficiency and specialization. This structure ensures tasks are managed effectively within each department, enhancing productivity and organizational performance.
#3. Multi-Divisional Organizational Structure
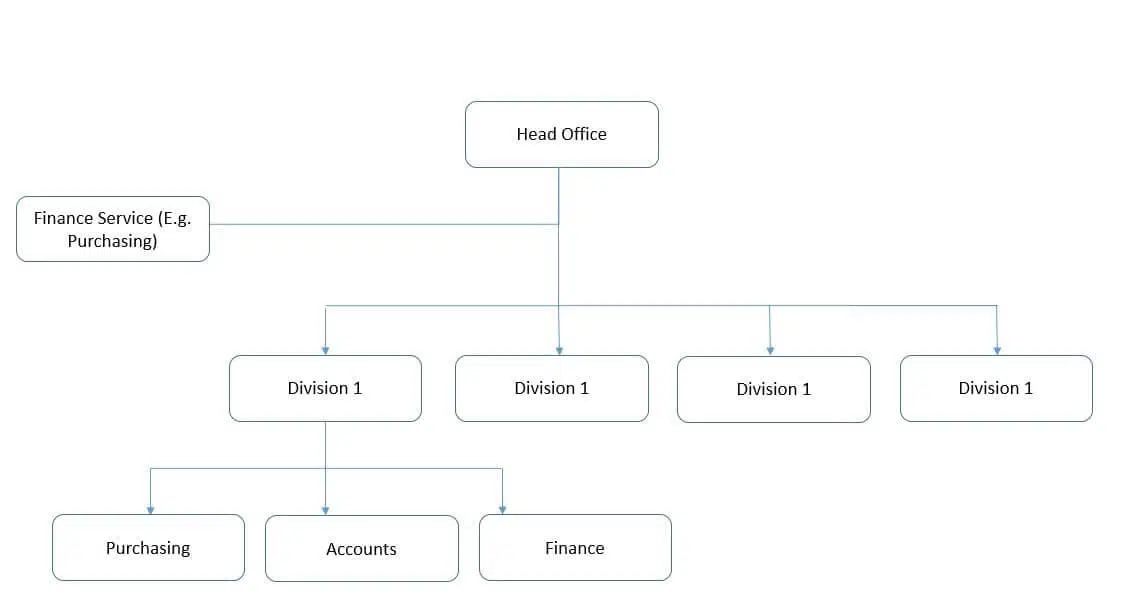
A multi-divisional organizational structure consists of several independent divisions, each focused on similar products or services. These divisions have diverse, skilled employees and resources to operate independently. While project managers oversee part-time staff, they have limited authority. Centralized oversight ensures coordination and alignment with overall organizational goals.
#4. Matrix Organizational Structure
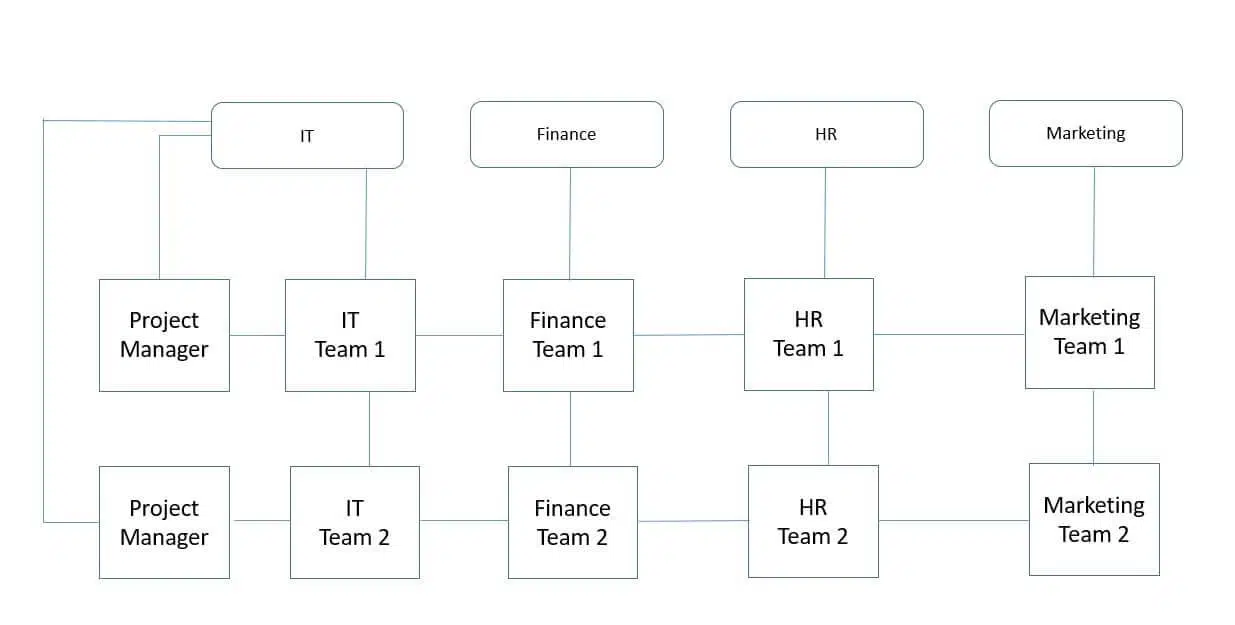
A matrix organizational structure combines functional and projectized structures, creating two command systems: vertical (functional) and horizontal (project). Employees work in both functional groups and specific projects, allowing resource sharing and collaboration. This structure offers flexibility and efficiency, making it one of the most popular choices for organizations.
You can divide it into three types:
(I) Strong Matrix Structure
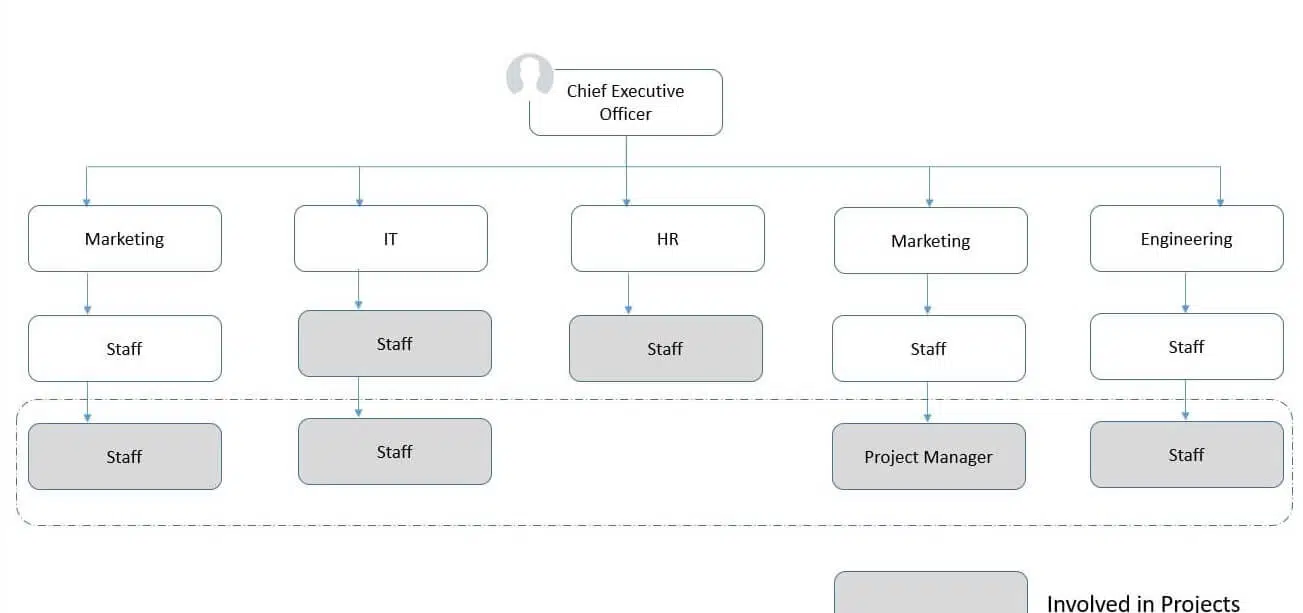
A strong matrix structure closely resembles a projectized organization. In this structure, project managers hold the highest authority and have significant control over resources and decision-making. Functional managers have a limited role, focusing on delivering successful projects efficiently under the project manager’s leadership.
(II) Balanced Matrix Structure
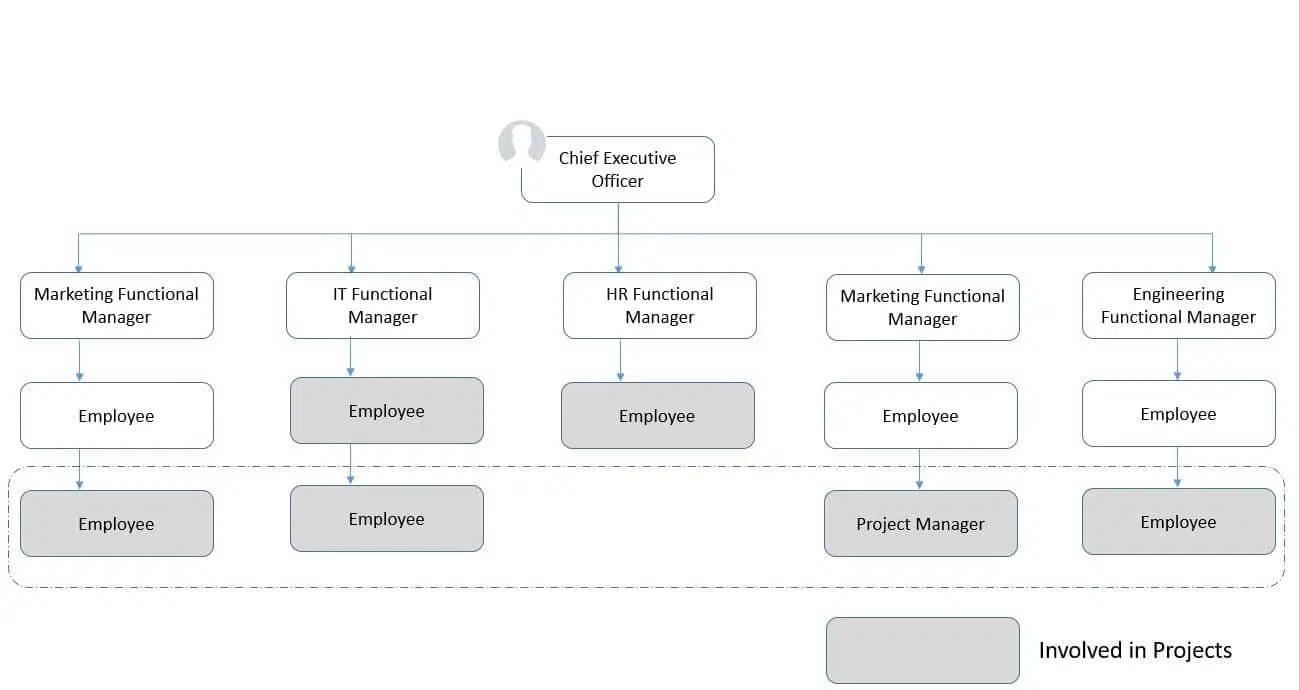
A balanced matrix structure equally blends functional and projectized organizations. In this setup, project managers and functional managers share authority and resources. Both work collaboratively to allocate tasks and ensure efficient project execution while maintaining functional expertise, creating a well-coordinated and balanced management approach.
(III) Weak Matrix Structure
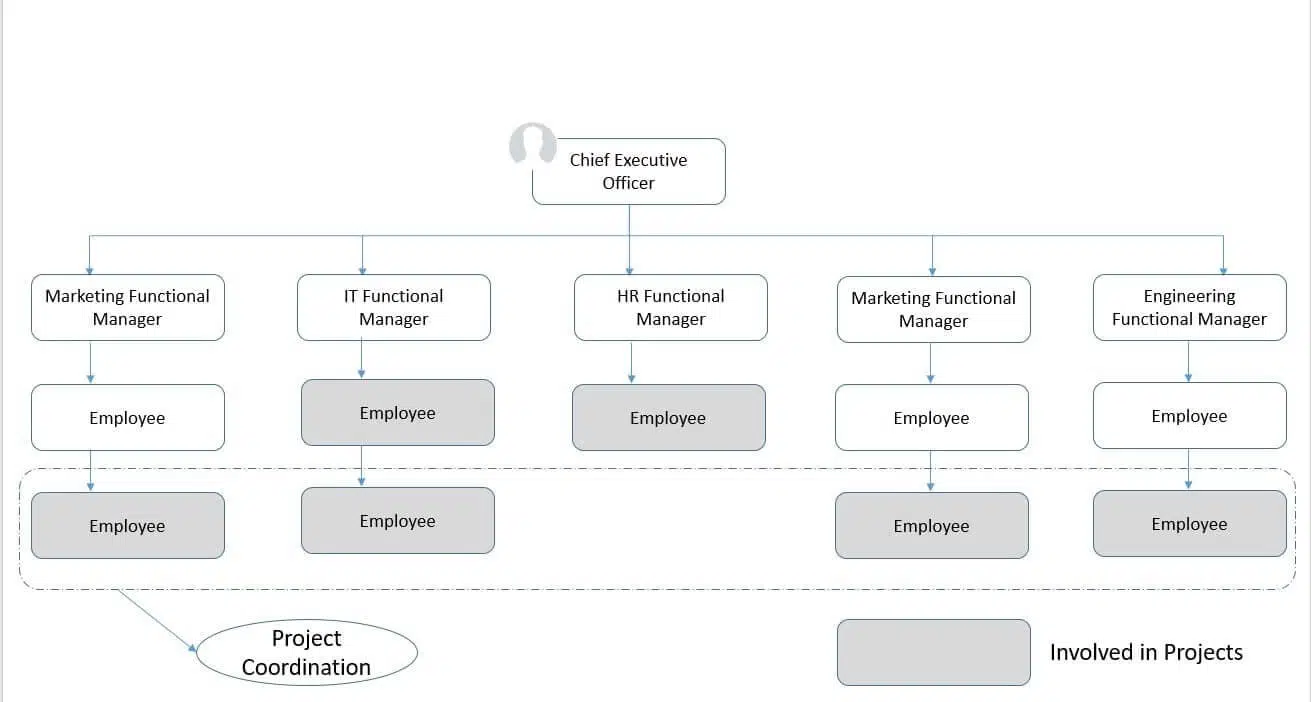
A weak matrix structure closely resembles a functional organization. In this setup, the functional manager holds full authority and controls resources, while the project manager has minimal authority. The project manager primarily coordinates tasks but relies on the functional manager for decision-making and resource allocation.
#5. Project-Oriented (Composite or Hybrid) Organizational Structure
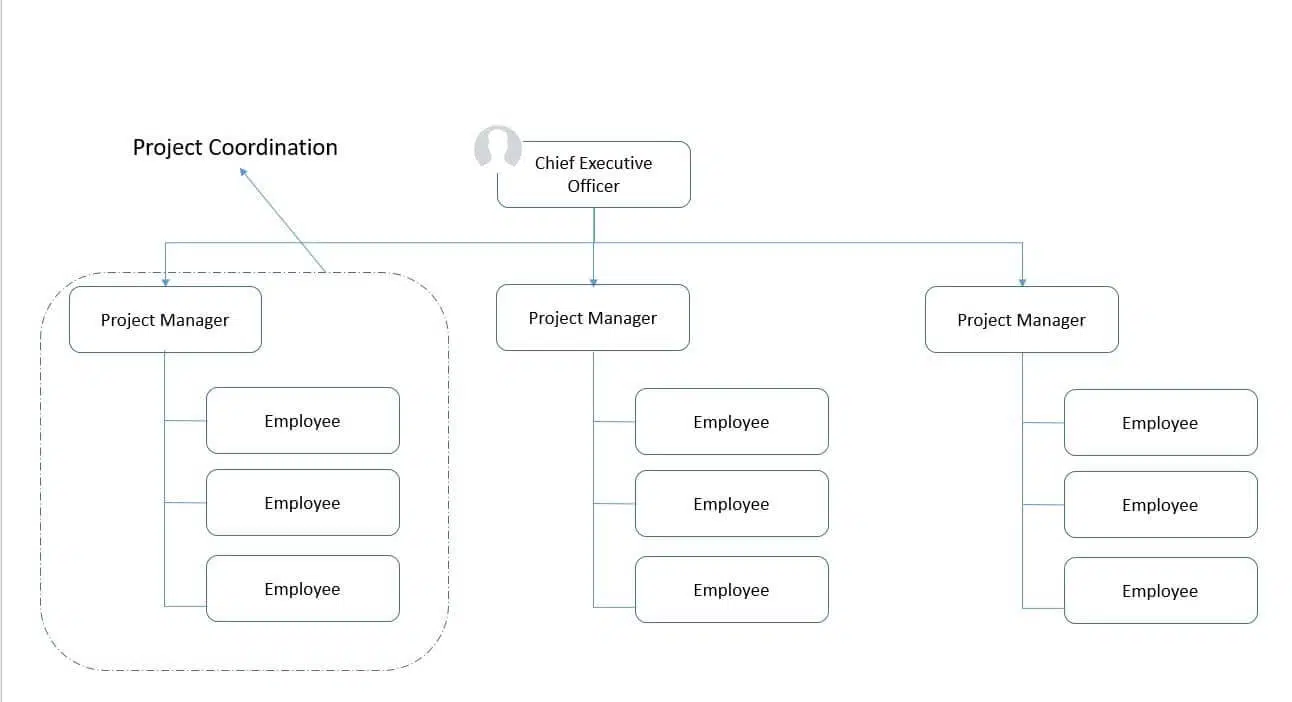
A project-oriented (composite or hybrid) organizational structure focuses solely on projects. The project manager has a full-time role, complete authority, and control over all resources. This structure is common in small to medium-sized organizations dedicated to project-based work, ensuring efficient management and successful project delivery.
#6. Virtual Organization or Network Structure
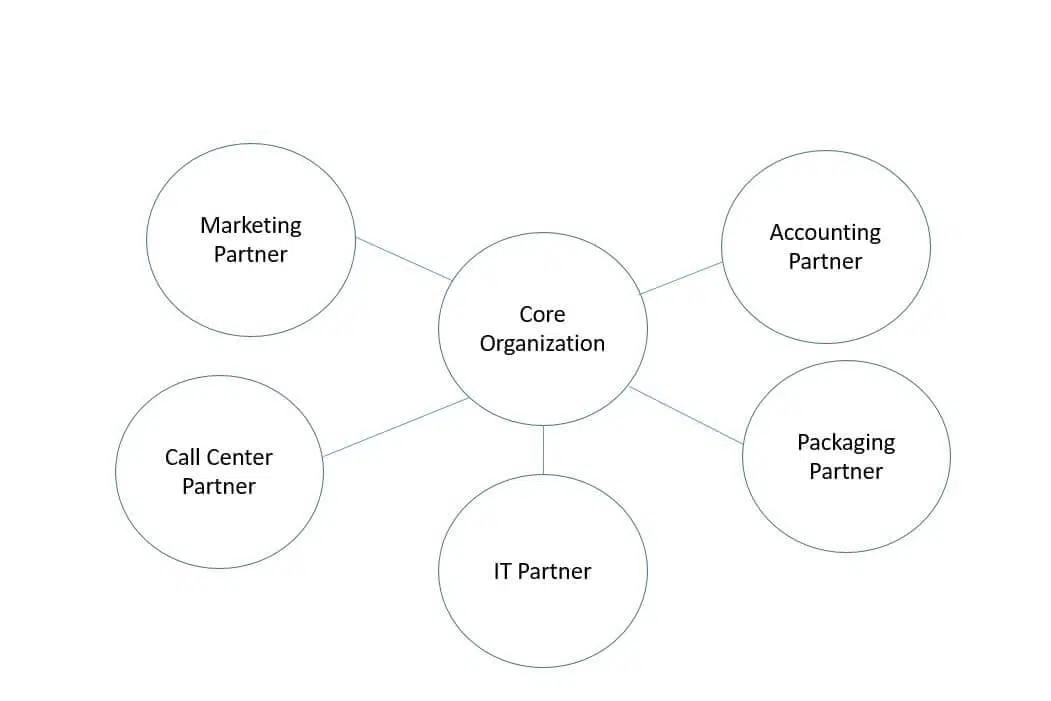
A virtual organization or network structure focuses on core business functions while outsourcing non-essential tasks via the Internet. This model drives corporate growth and profitability. Project managers in this structure have low-to-moderate authority and limited control over resources, relying on external partners for various operations and services.
#7. Hybrid Organizational Structure
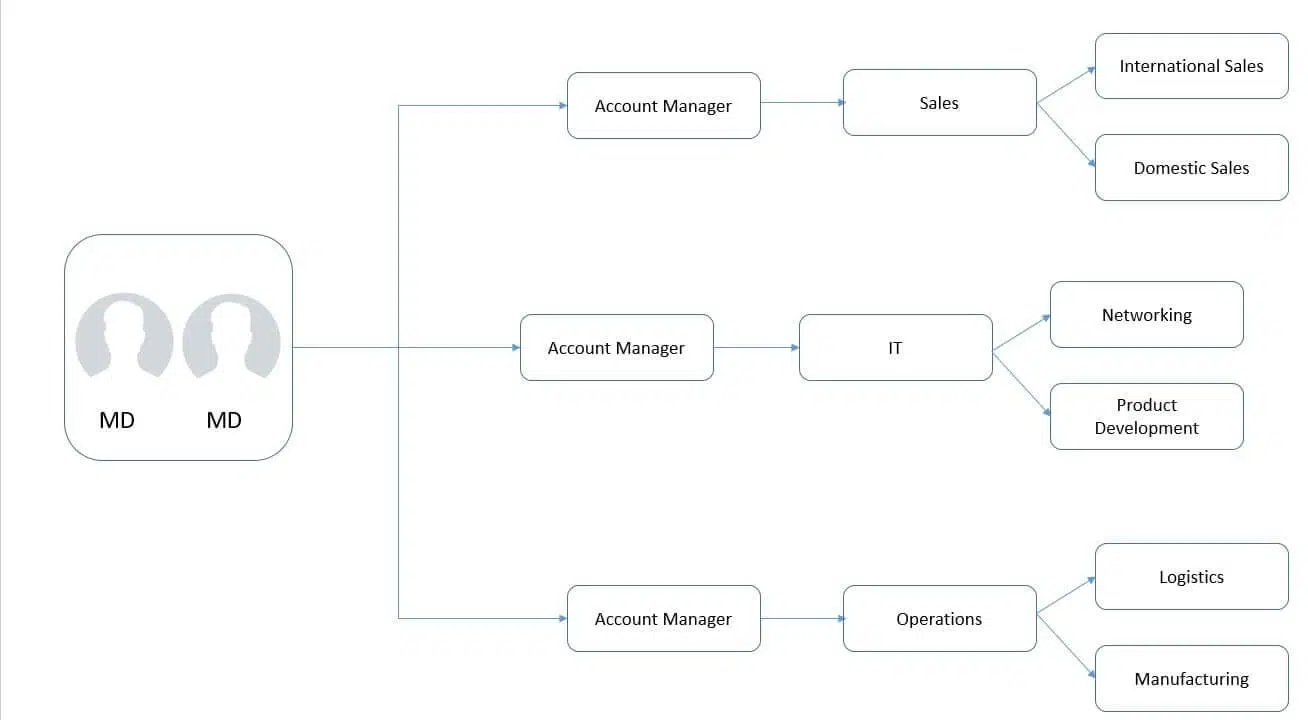
A hybrid organizational structure combines elements of various organizational types to meet diverse needs. It allows flexibility, with responsibilities, authority, and resource control tailored to each situation. This approach is ideal for organizations with complex or varied requirements, enabling them to adapt and function efficiently across different areas and projects.
#8. PMO (Project Management Office)
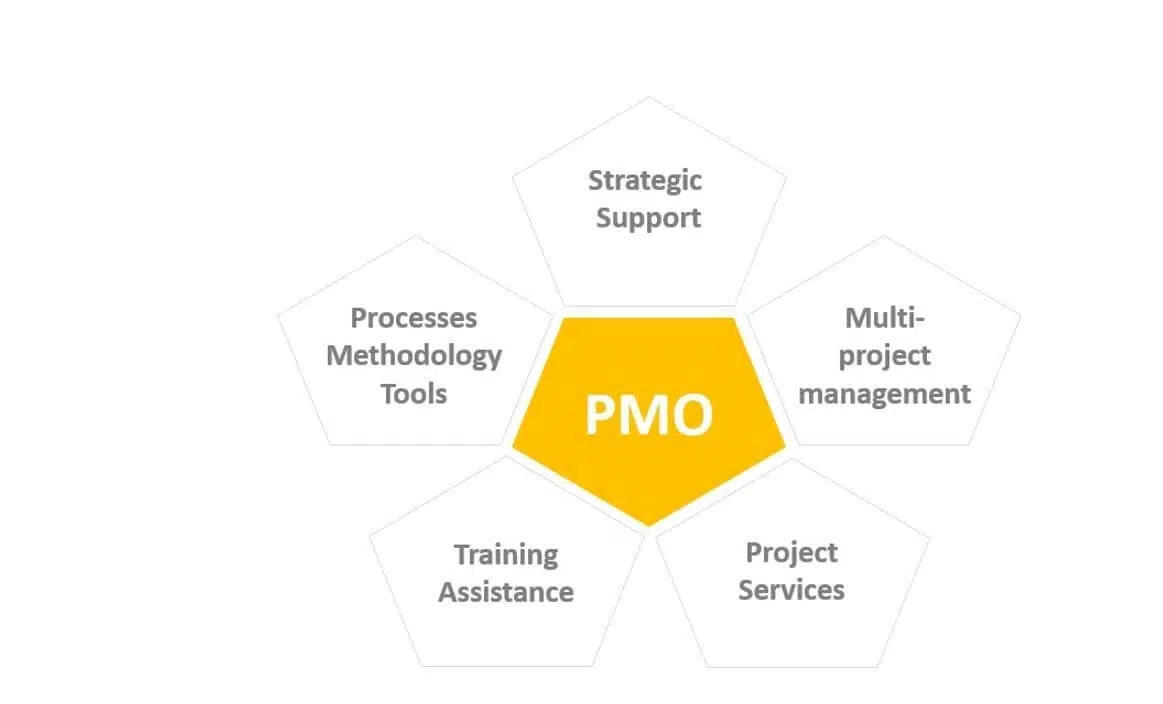
A Project Management Office (PMO) is a mixed organizational structure where project managers have full authority and control over resources. It centralizes project management practices, ensuring consistency, governance, and efficient project execution across the organization. The PMO supports alignment with strategic goals and enhances overall project performance.
Importance of Organization
An organization is important because it helps businesses work efficiently. It creates a system to easily manage tasks, give instructions, and control workflow. Below are the key reasons why organization is important:
- It Optimizes Resource Utilization: Organizations ensure that resources like time, money, and manpower are used effectively, reducing waste and increasing productivity.
- It Makes Administration Easy: A well-organized system simplifies management. It helps leaders plan, make decisions, and monitor work without confusion.
- It Improves Employees’ Skills: Organized businesses provide clear roles and training. This helps employees learn and improve their skills over time.
- It Helps Grow Business: An organized business can expand easily. Structured processes allow the company to handle more work and customers.
- It Motivates Employees and Builds Culture: The organization creates a positive work environment. Employees feel motivated when tasks are clear and teamwork improves.
Summary
An organization is a collective of individuals united by a common goal. Whether hierarchical, functional, or flexible, the chosen structure is crucial in supporting the organization’s mission, values, and vision. A well-designed structure ensures alignment of efforts, efficient resource use, and clear direction. Priorities within the organization guide activities, helping it adapt to changing needs and focus on achieving long-term objectives.
The structure must support collaboration, coordination, and productivity, helping the organization fulfill its purpose while maintaining its core principles.
