Have you ever considered taking out a payday loan to cover an urgent bill? These small, short‑term loans can seem like a quick fix, but they are one of the costliest forms of credit available. According to the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau, a payday loan is usually a short‑term, high‑cost loan of $500 or less that must be repaid on your next payday. The following guide explains how payday loans work, who qualifies, the true costs involved and better options when money is tight.
What is a Payday Loan?
A payday loan is a cash advance designed to bridge the gap between paychecks. Lenders give the borrower a small amount of money (often under $500) and expect repayment when the borrower receives their next wage, pension or benefit payment. Most payday loans share several features:
- Small loan amounts. State laws often cap payday loans at around $500.
- Short terms. The loan is typically due in a single payment two to four weeks after it is made.
- Automatic repayment. Borrowers provide a post‑dated check or authorize the lender to electronically debit their bank account.
- Minimal credit check. Payday lenders do not usually verify the borrower’s ability to repay while meeting other expenses.
Because of these factors, payday loans are easy to obtain but can be extremely expensive. State laws limit fees to roughly $10–$30 for every $100 borrowed, which results in an annual percentage rate (APR) approaching 400%—far higher than credit cards or installment loans.
How Payday Loans Work
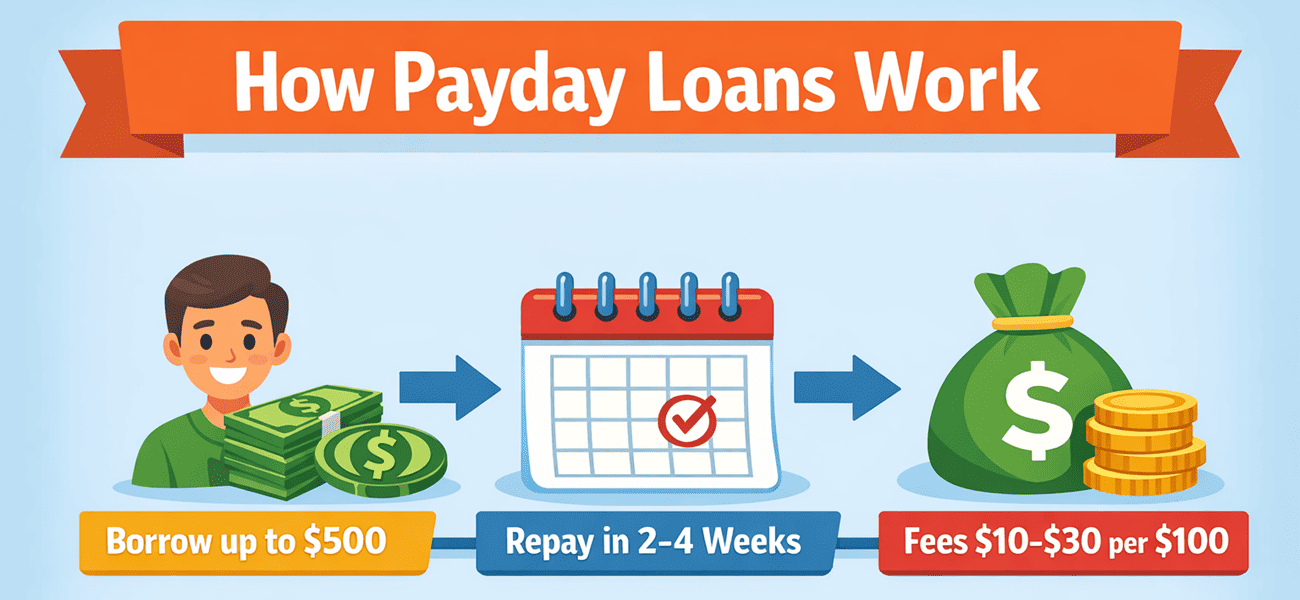
Borrowing from a payday lender follows a straightforward process:
- You apply for a small loan. The lender asks for proof of income, government identification and a bank account.
- You receive cash quickly. Funds are paid via cash, check or electronic deposit, often within minutes. Loan amounts are small because many states cap payday loans at a few hundred dollars.
- You repay on your next payday. Repayment is due in one lump sum within two to four weeks. The lender withdraws the loan amount plus a fee from your bank account on the due date. If you cannot repay, some lenders allow you to roll over the loan, which adds another fee and extends the due date.
Payday loans are marketed as convenient for unexpected expenses, but the short repayment window and high fees make it difficult for many borrowers to pay on time. Repeat borrowing can lead to a costly debt cycle.
Who Can Qualify?
The requirements for a payday loan vary by state but generally include:
- Age and identification. You must be at least 18 years old and provide a government‑issued ID (driver’s licence or passport).
- Proof of income. Lenders usually ask for a recent pay stub or benefits statement to confirm that you have steady income.
- Active checking account. Most lenders require a bank account so they can deposit funds and withdraw repayment. Without a bank account, you may have to visit a storefront and pay higher fees.
- Current contact details. Your home address, phone number and email are needed for communication and verification.
Payday lenders seldom check credit scores. Instead they base the loan amount on your income and state law. In California, for example, the average payday loan was $250 in 2023, with an average APR of 367% and a term of 16 days.
Fees and Real Costs
Even though payday loans are small, the costs add up quickly. State laws typically allow lenders to charge $10–$30 per $100 borrowed. A common fee is $15 per $100, which translates to an APR of nearly 400%. Here are common costs:
- Flat fee. Most payday lenders charge a single fee for the loan instead of a traditional interest rate. For example, borrowing $300 may cost $45 in fees.
- Rollover or renewal fee. If you cannot repay on the due date, the lender may allow you to renew the loan for another period and charge another fee. Renewals multiply costs and keep borrowers in debt.
- Late fee. Failing to repay or return the lender’s calls may result in additional late fees or collection charges.
Some states prohibit rollovers or require lenders to offer extended repayment plans. Always read the loan agreement carefully and calculate the total amount you will owe.
Who Uses Payday Loans?
Contrary to popular belief, payday loans are not limited to unemployed borrowers. The Federal Reserve’s 2023 survey of household economics found that 6% of adults used a payday, pawn, auto title or tax refund anticipation loan in 2023, up from 5% in 2022. Usage was highest among people with lower incomes: 10% of adults with household income below $25,000 and 10 % of those earning $25,000–$49,999 used one of these products. By comparison, only 2% of adults earning $100,000 or more did so. The survey also found higher usage among Black (10%) and Hispanic (11%) adults compared with White (3%) adults. These statistics show that payday loans disproportionately affect communities with limited savings and credit access.
Many borrowers turn to payday loans for recurring needs—rent, groceries, utility bills—rather than one‑time emergencies. When budgets are already stretched, the high fees can make repayment difficult, leading to repeat borrowing and mounting fees.
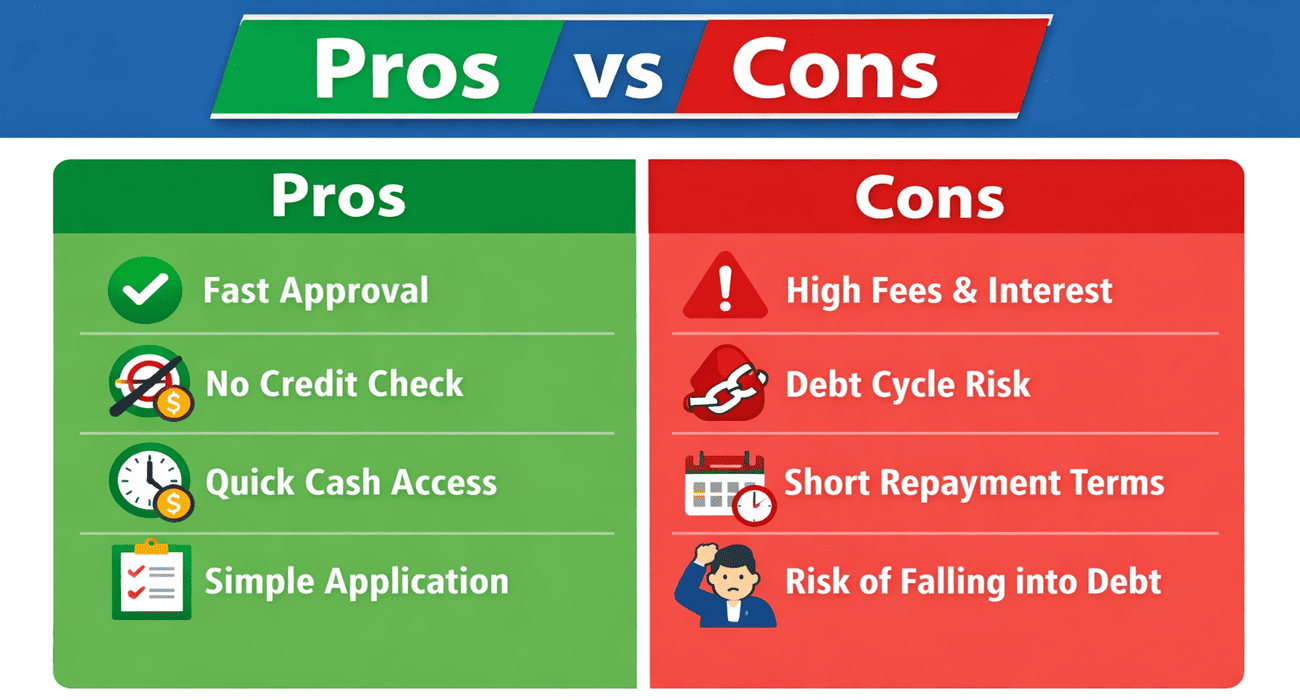
Pros of Payday Loans
Despite their downsides, payday loans offer a few advantages:
- Fast approval and funding. Applications are short, and funds may be available on the same day.
- No credit check. Borrowers with poor credit may qualify because lenders focus on income.
- Accessibility. Payday lenders operate storefronts and online platforms, making them easy to find in many states.
Cons of Payday Loans
The disadvantages of payday loans outweigh the benefits for most borrowers:
- High costs. Fees of $10–$30 per $100 borrowed result in interest rates approaching 400 %.
- Short repayment window. Payments are due within two to four weeks, often before the borrower has recovered financially.
- Risk of debt cycle. Borrowers who cannot repay may renew the loan and pay additional fees, creating a cycle that is difficult to break.
- Limited loan amounts. State laws cap loan amounts, so a payday loan cannot cover large expenses.
Alternatives to Payday Loans
Fortunately, several safer options exist:
- Negotiated payment plans. Contact your landlord, utility company or medical provider to ask for an installment plan. Many providers will work with you to prevent service interruption or eviction.
- Credit union small‑dollar loans. Many credit unions offer payday alternative loans (PALs) with lower fees, longer terms and amounts up to $2,000. Membership is often inexpensive.
- Personal installment loans. Banks and reputable online lenders offer personal loans with lower APRs and manageable monthly payments. Borrowers with good credit may qualify for rates below 30 %.
- Borrow from friends or family. A small loan from someone you trust may provide relief without high fees. Put the terms in writing to avoid misunderstandings.
- Local assistance programs. Non‑profit organizations, churches and community groups sometimes provide emergency funds or short‑term loans to help cover essential expenses.
Protecting Yourself When Using a Payday Loan
If you decide to use a payday loan, take steps to reduce the risk:
- Borrow only what you absolutely need and avoid multiple loans at once.
- Compare lenders and choose one that is licensed in your state; unlicensed lenders may not follow consumer protection laws.
- Read the entire loan agreement. Understand the fee structure, due date and whether rollovers are allowed.
- Set aside the repayment amount in your budget so you can pay on time.
- Check if your state requires lenders to offer extended repayment plans. If you cannot repay, contact the lender immediately and ask about payment arrangements.
Regulation and Legal Status
Payday lending is legal in many U.S. states, but laws vary widely. Some states have banned payday loans entirely or capped interest rates at 36% or lower, while others allow higher APRs. Servicemembers and their families are protected under the federal Military Lending Act, which caps the military annual percentage rate (MAPR) at 36% and prohibits certain fees. Always verify the legal status of payday loans in your state before applying.
FAQs
Q1. Are payday loans legal everywhere?
No. Some states ban payday lending or cap interest rates at 36 %. Check your state’s regulations before applying.
Q2. How much can I borrow with a payday loan?
State laws usually cap payday loans at around $500. In California, the average loan in 2023 was $250.
Q3. What happens if I cannot repay on the due date?
You may incur rollover fees or late charges. Ask the lender about extended repayment plans or consider negotiating with them before missing the payment.
Q4. Do payday lenders check credit scores?
Payday lenders generally do not perform traditional credit checks; they base approval on income and state requirements.
Q5. What are safer alternatives to payday loans?
Try negotiating payment plans with billers, applying for a credit union small‑dollar loan, seeking a personal installment loan, or contacting local assistance programs.
Conclusion
Payday loans can offer fast cash during short-term emergencies, but they come with high fees, short repayment periods, and real risks. Before borrowing, it is important to understand how these loans work, who they are meant for, and the true cost of repayment. Exploring safer alternatives, planning ahead, and borrowing responsibly can protect your finances. Making informed choices helps you avoid debt cycles and build stronger, more stable financial habits over time for long-term security and peace of mind always.
