A PESTLE analysis studies vital external factors (political, economic, sociological, technological, legal, and environmental) that influence an organization and help guide management to make strategic decisions.
Businesses use this technique to scan their current or prospective environments, especially when planning to launch a new project, product, or service.
Every organization focuses on growth. However, competition is so fierce that any wrong move can be disastrous. Therefore, businesses must closely monitor every decision and perform a proper analysis.
Organizations can manage internal factors, but driving external factors is beyond their control.
Political situations, governmental regulations, technological improvements, environmental concerns, legitimacy of activities, commerce, and sociological factors play a role.
PESTEL analysis helps businesses review these factors.

Earlier, it was known as PEST analysis. Later, legal and environmental factors were added, and now experts debate adding ethics into the framework.
Why is PESTLE Analysis Used?
PESTLE analysis studies how various factors affect a startup or a new business.
It examines the impact of politics, economics, society, technology, law, and environments on new businesses. This analysis helps organizations understand how smoothly they can operate with the factors.
PESTLE analysis is essential in business planning as it helps organizations understand the risk factors associated with a business.
This analysis also provides insight into policies, such as decisions and policies regarding suitable business location, product development, marketing planning, staff and workforce recruitment, planning, and other organizational changes.
Small and large businesses use PESTLE analysis to determine trends. It helps assess scalability options, possibilities, and whether the value or service will remain relevant in the long term.
The Six PESTLE Factors
1. Political
Political factors include taxation, ecological regulations, trade constraints and deregulation, taxes, and social stability. This factor focuses on how political conditions in a country can affect the business, like tax restrictions, custom rules, and non-tariff hurdles (like minimum import prices and export bans).
It also includes penalties for tax-related offenses such as tax fraud.
Industry regulations that refer to laws regarding the operation of specific types of businesses can be political factors.
Agreements and restrictions concerning global and international trade guidelines or foreign policy.
2. Economic
Economic issues play a significant role in business decisions. Growth, cost of living, top-quality trade, hyperinflation, access to credit, wage levels, unemployment (local and national), minimum wage, and working hours are a few examples of economic factors.
Inflationary pressures in any industry can influence the product pricing structure. It affects consumers’ bargaining capacity and causes a shift in the country’s economic demand/supply patterns.
3. Social
Social norms and preconceptions, health consciousness, demographic growth rates, age distribution, vocational choices, well-being, and safety are critical factors for businesses to evaluate. These elements are crucial for advertisers to understand if they wish to attract a specific audience.
Social factors help businesses make plans that distinguish them from competitors.
Analyzing social factors helps organizations understand individual lifestyle choices and population demographics such as age, gender, cultural principles, consumer tastes, and buying habits.
4. Technological
This factor examines how a business responds to technological advancements and how this is reflected in its products and services. It considers how innovations will affect security and data storage.
Technical aspects are advances and discoveries; these factors greatly affect business operations. Artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, computer vision, and pattern recognition ensure the corporation maintains its market advantage.
Disruptive technologies are also analyzed. This includes smartphones, robotics, and automation. The increasing shift towards artificial intelligence is also studied in this category.
5. Legal
This factor considers labor laws and employment regulations that affect working practices. It focuses on legislation and regulations regarding health and safety environments. Progress in the legal landscape is also monitored.
In addition to these rules and norms, organizations establish choices and regulations that their delegates must follow.
6. Environmental
These criteria assess the impact of ecological and environmental factors, such as laws on energy use, environmental preservation, and refuse management.
Environmental degradation and transitions to renewable energy compel every company to address ecological factors. Because of this, firms must now engage in Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR). This PESTLE component is critical for specialist industries such as ecotourism, agriculture, and agribusiness.
Environmental factors examine whether a business directly impacts the environment.
PESTLE Analysis Process
1. Determine the Research’s Scope
This is the first step. The scope analysis should examine the possible business scenarios, both present and future. It should be feasible and applicable to the business industry and locations.
2. Data Collection
Identify multiple people to collect data to bring in a variety of evidence and viewpoints and determine how it will be gathered. Analysts seek the best sources when scouting for information.
3. Data Analysis
The following steps ensure correct data analysis:
- Assign a value to each item based on its potential risk to the organization.
- Determine alternatives for handling business problems.
- Document all findings for further discussion.
- Inform decision-makers and stakeholders of findings.
- Find the necessary activities and identify trends that must be tracked.
PESTLE analysis can aid in the early detection of trends and create a competitive advantage. A couple of PESTLE analysis templates are available online and can be utilized to record information.
PESTLE Analysis Template
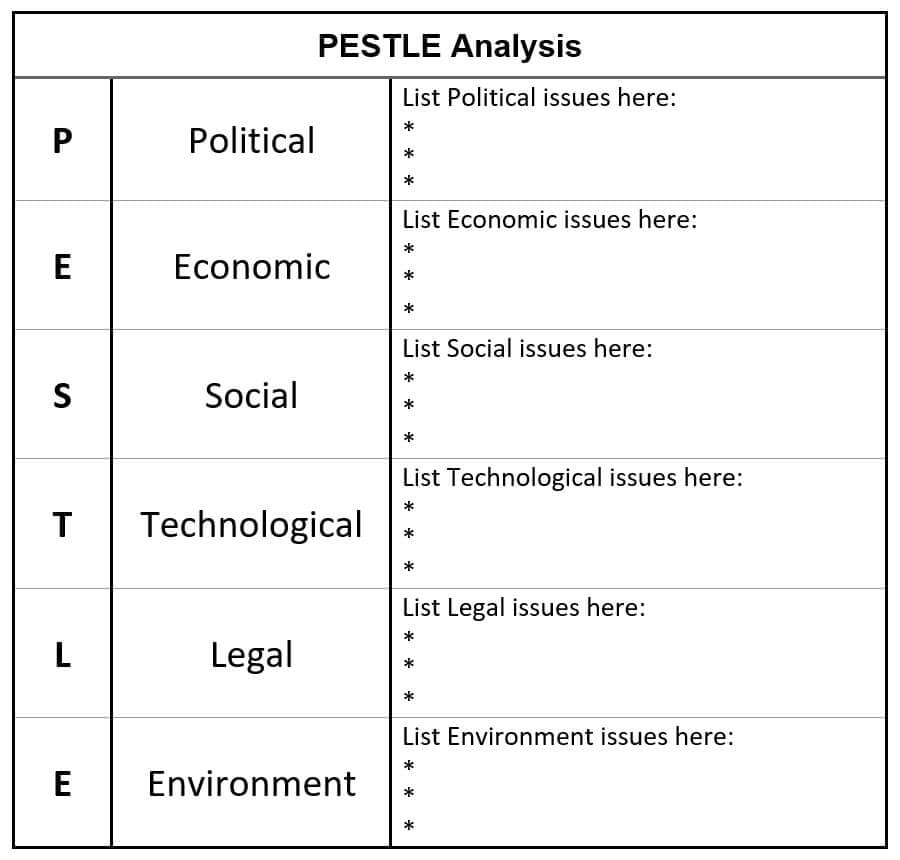
Advantages of PESTLE Analysis
- Comprehensive View: PESTLE provides a holistic overview of the external factors that can impact an organization. It helps businesses see beyond internal operations.
- Strategic Insight: Analyzing political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors aids in strategic decision-making and long-term planning.
- Risk Identification: It helps identify potential risks from the external environment, enabling proactive mitigation strategies.
- Opportunity Recognition: Identifies emerging opportunities in the macro-environment, such as technological advancements or social trends.
- Industry-Agnostic: This can be used across industries, making it versatile and widely applicable.
- Supports Innovation: Highlights technological advancements and evolving consumer needs, encouraging innovative solutions.
- Aids in Scenario Planning: Useful for businesses preparing contingency plans by exploring different macroeconomic scenarios.
- Decision Support Tool: Provides a structured framework for evaluating the external environment before making critical decisions.
Limitations of PESTLE Analysis
- Time-Consuming: Conducting a detailed PESTLE analysis requires substantial time and effort, especially in rapidly changing environments.
- Complex Interdependencies: Overlapping factors (e.g., Political and Legal) can complicate the analysis, making it hard to isolate single influences.
- Subjectivity: The interpretation of factors can vary among analysts, leading to inconsistent or biased conclusions.
- Lack of Prioritization: PESTLE identifies many factors but does not provide a way to prioritize their importance or likelihood.
- Data Dependence: The analysis’s effectiveness relies heavily on the accuracy and recency of data, which can sometimes be challenging to obtain.
- Limited Predictive Power: PESTLE provides insights into trends but cannot precisely predict future events or their impacts.
- Broad Scope: It focuses on macro-level factors and may not address specific micro-level industry challenges.
- Static Snapshot: As external factors change rapidly, the analysis can quickly become outdated unless revisited frequently.
Conclusion
PESTLE analysis is a valuable tool for organizations to prepare them for difficulties. Whether growing a line of products or creating a new organization in a new region, PESTLE analysis is critical in formulating plans and strategies.
PESTLE analysis offers a holistic overview of a business’s surroundings and all key aspects that may affect the work. It is the foundation of an organization, defining the factors that affect its goals. It’s deeper than just knowing how to read a market. Research has shown that companies that swiftly detect and adapt set themselves apart.
Reference:
