Predictive analysis came to the spotlight in the 1940s, when governments and organizations started using computers and technical models to improve their performance. Predictive analysis helps businesses find patterns to identify risks, opportunities, strengths, and threats.
This article will explain the predictive analysis and how an organization can use it beneficially.
What is Predictive Analysis?
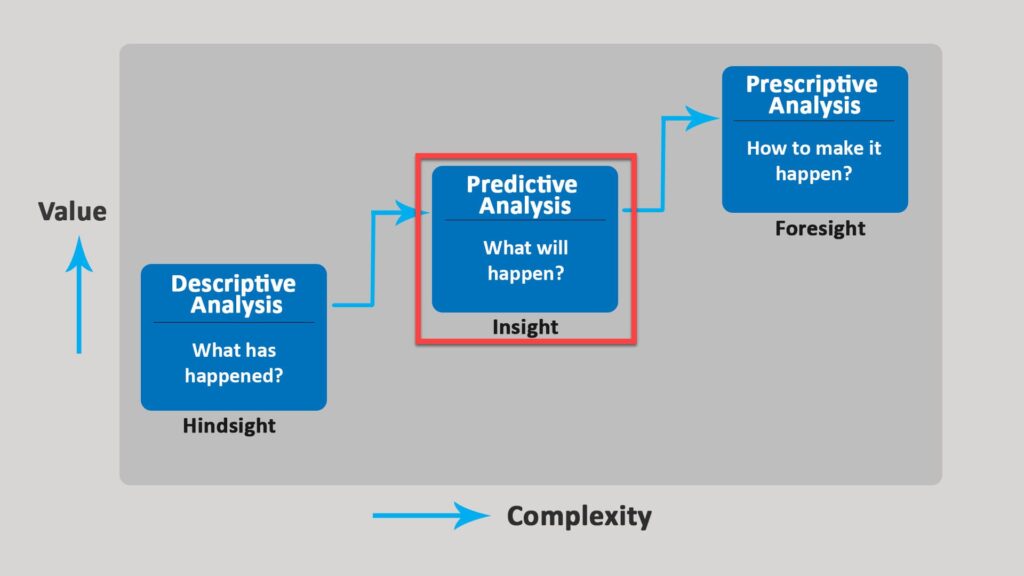
Definition: Predictive analysis lets businesses predict future outcomes using historical data. Companies can use customer feedback or responses, promote cross-selling opportunities, and improve business processes. Predictive analysis helps businesses keep their customers and attract new ones.
Some Most Common Predictive Analysis Models are:
1- Neural networks help in identifying relationships between two or more data sets using automated algorithms
2- Decision trees indicate a possibility from each outcome by using the branching technique
3- The clustering model separates data into groups with similar attributes. It lets companies build strategies for personalized groups.
4- The forecast model uses metric value prediction to devise learning. They are based on historical valuations and predict prospects.
5- Classification models provide an answer to yes/no type questions. It puts data sets in different categories based on historical findings.
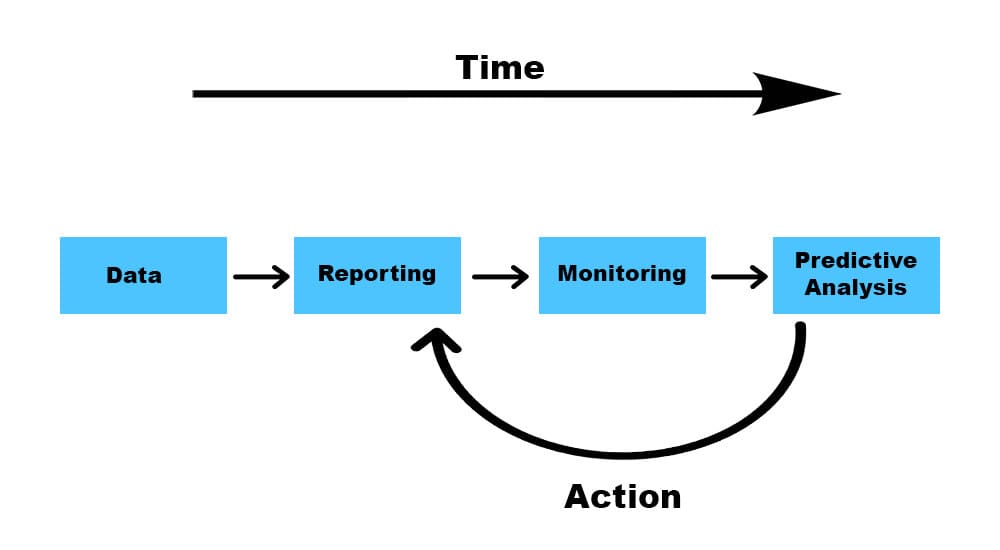
How Does Predictive Analysis Work, and What is it Used For?
Predictive analysis uses software that combines several variables into the predictive model. It analyzes and predicts the future probability of outcomes. The software is equipped with advanced algorithms and techniques to make the outcome reliable. The historical data should not be outdated or inaccurate.
Predictive Analysis in Businesses is Used for Several Purposes Like
- Each activity on a company’s network is monitored in real time, and any abnormality is detected through predictive analysis. This helps businesses identify potential fraud. Thus preventing the company from witnessing any cybercrimes or attacks.
- Predictive analysis helps businesses improve their operations. This is done through forecasting inventory management and resource allocation. Resulting in a more effective and efficient process.
- Businesses can use customer feedback towards the product or service they offer to create better quality products and retain customers. Marketing campaigns can be optimized to serve customers more personalized manner.
- The predictive analysis provides companies with the credit scores of consumers. This helps the business understand its default probability. Analyzing an individual’s creditworthiness allows businesses to reduce risk.
Benefits of Using Predictive Analysis
Improves Business Performance
Businesses can find their most profitable areas using predictive analysis. They consider their profitability and customer satisfaction to identify the proper channels for improving business performance.
Identifies Potential and Profitable Customers
A loyal customer base is a key to business success. Predictive analysis helps identify customers who spend on the business. Customers who spend are the best for the business in the long term. The insights provided by predictive analysis allow companies to enhance and optimize marketing strategies for these audiences. They also focus on acquiring and retaining customers. This increases customers’ lifetime value.
Predicts Potential Risks
A predictive analyst can forecast risks by identifying market patterns and trends in the industry. This is done by analyzing historical data and the current state of the business.
The analytics provide risks the business can face. This helps businesses focus on critical risks, identify threats, assess the impact on the company, and decide the plan of action to manage these risks.
Performs Data Maintenance
The more an organization conducts a predictive analysis, the more it collects data set. This is because regular predictive analysis requires updating data continually. Companies can perform maintenance activities by using advanced software. They capture, analyze and organize generated data.
This helps control preventative maintenance costs, avoid downtime and improve business assets’ life.
Enhances Customer Segmentation
Customers can be segmented based on:
- Geographical location,
- Purchasing power,
- Specific requirements and more
Predictive analysis uses customer behavior and interaction to categorize them into the right areas.
Increases Customer Retention
Predictive analysis improves customer retention. They assist in bringing new customers and identifying profitable ones. Since it is more expensive to bring in new customers than to retain the existing ones, predictive analysis helps prevent customer churn. It also improves customer retention.
It does so by identifying:
- Why customers are unsatisfied
- What the business can do better
- Which customer segments are most prone to leave
- Which segment is the most profitable, and similar aspects
After analyzing this information, businesses can take necessary actions to increase customer satisfaction and business revenue.
Stay Ahead in the Industry
Predictive analysis helps businesses forecast future patterns and market trends. This lets businesses make informed decisions to stay ahead of the industry. They do so by forecasting prospects through reliable data.
Features of a Predictive Analysis Model
1- Defined Business Objective
Predictive analysis can calculate default estimates, customer identification, retention projections, fraud detection, attrition, and more. It helps define objectives considering all factors and available resources.
2- Performance Metrics
Predictive analysis can be successfully developed when coupled with business performance metrics. Each model is evaluated with respect to the performance metrics. This helps companies make the right decisions in the business environment.
3- Resource Allocation
Business processes require efficient resource allocation. When allocating time or money in a business leads to negative performance metrics, there is an opportunity to use predictive analysis.
Businesses can optimize and adjust their resource allocation strategies to improve business performance.
4- Enough Data
The predictive analysis depends on historical data. Data availability is a key requirement for successful business analysis. If the available data is insufficient, predictive analysis techniques will not provide accurate results. This will lead to poor decisions.
Quantitative models need a thousand records to help businesses identify opportunities.
5- Specific Interest Behavior
Behavior interest can affect the output of the business analysis. This is because predictive analysts consider historical data that represents the type of behavior represented in each data set.
When the specific interest behavior consistently supports the business objectives, the project’s success is guaranteed. However, if the interesting behavior is not defined, the analysis can provide inaccurate results.
How to Implement the Predictive Analysis Process?
1. Identify Requirements
The first step in implementing the predictive analysis process is identifying the main business problem. In this step, business analysts must be clear about the business objective. This helps in the successful conduction of the analysis.
Collect questions about the business issue and list them according to their priority. Address the most critical problem first. Businesses hire a statistician or professional analyst at this stage, too. This helps in measuring success and enhancing performance after analyzing historical data.
2. Explore Market Data
A professional analyst can quickly identify data that addresses the business’s problem. After exploring the market data, the analyst chooses the best data that suits the situation. Data suitability, relevancy, accuracy, cleanliness, and quality are critically examined at this step.
3. Develop a Model
Developing a predictive model includes figuring out which model best suits the business objectives, culture, and problem. Analysts experiment with different models, methodologies, features, algorithms, and processes before selecting the model. This helps them maintain the right balance between accuracy, reliability, performance, expansibility, etc.
4. Implement the Model into the Business
Once a model is finalized and historical data is analyzed, the analyst approves the model to determine the best method. This method helps to clean, retrieve, and transform the raw data into a finished one. At this stage, the predictive model can be deployed at a large scale. The deployment positively impacts the company’s organizational process and culture.
5. Validate/Confirm the Results
The last step in implementing the process is to monitor the models’ performance. Confirming the model’s result is critical to analyze whether applied changes have brought the desired result.
Organizational Example of Predictive Analysis
Let us consider that Mr. X is a data analyst working with ABC Pvt Ltd. the organization realizes that employee churn in the last five years has increased by 25%. To understand why employees are quitting jobs, Mr. X conducts a predictive analysis.
During this process, Mr. X analyzes:
- The salary hike in the last five years
- Annual reports of the company
- Employee satisfaction levels
- Compensation and benefit reports
- A few other reports concerning employee satisfaction.
After the analysis, Mr. X understood that turnover risk factors were being overlooked. This resulted in a non-retention of talent. There was also a lack of talent, upskilling workshops, and incentives. This led Mr. X to share the information with the managers to train them better, provide higher incentives and retain high-performing employees contributing positively to the company. After employing these strategies, the company noticed a significant drop in employee churn the following year.
However, the initiative also increased costs for the company by providing the employees with workshops, talent upskilling programs, and incentives which will benefit the company in the long-term and increase profitability.
Summary
Predictive analysis helps businesses gain a competitive and comparative advantage, identify fraud, open new opportunities, improve productivity, and more. It is one of the strongest analyses that provide the business with future-driven information and enables it to decide accordingly.
A holistic predictive analysis can attract and retain the most profitable customers. Businesses can manage resources effectively after analyzing their historical data and comparing it with their current position for better future performance.
