Every organization wants to get better at what it does. Yet many teams struggle to know how they compare to industry leaders. That is where process benchmarking comes in. By looking outward and measuring your processes against best‑in‑class performers, you can find gaps, learn new practices and design a plan for improvement.
Did you know that a study found that one‑third of organisations do no benchmarking at all while only 31% benchmark both internally and externally? If your company falls into those groups, this guide will help you catch up.
What is Process Benchmarking?
Benchmarking means comparing your business performance with that of industry leaders to see where you stand. Benchmarking involves “comparing a company’s performance metrics with those of industry leaders or best‑in‑class businesses” across productivity, efficiency, quality and cost. Process benchmarking focuses on specific operational processes rather than the whole organisation.
Instead of asking “How is our business doing?” you ask “How is our procurement process compared with the best in our industry?” This narrow focus makes it easier to find actionable insights.
The goal of process benchmarking is not simply to copy another company’s approach. It is to understand why they perform better, adapt their techniques to your context, and create a culture of continuous improvement. By measuring yourself against a standard, you know what excellence looks like and can set realistic targets for your team.
Why Process Benchmarking Matters
Competition is fiercer than ever, and customer expectations change quickly. Regular benchmarking offers several benefits:
- Defines success with data: Benchmarking helps you set measurable targets rather than vague goals. For example, you might aim for a 10 % increase in on‑time deliveries after seeing that industry leaders achieve 15 %.
- Reveals performance gaps. Comparing your process cycle time or defect rate with a rival’s highlights where you need improvement. If your competitor releases eight product features for every three you deliver, the gap is clear.
- Raises quality standards. When you discover that a peer hosts four customer events per year and you host two, you can decide if increasing engagement will improve customer satisfaction.
- Supports informed decisions. Benchmarking data guides investments and process changes, reducing guesswork.
- Encourages continuous improvement. Regular comparison fosters a culture of excellence where teams strive to meet or exceed best‑in‑class standards.
Types of Process Benchmarking
Benchmarking comes in several forms. Understanding each type helps you choose the right approach for your goals.
There are three main types:
- Internal benchmarking compares your processes with those of other departments or past projects within your organisation. It is useful when you control data collection and want quick wins. For example, your logistics team might learn from your customer service team’s way of tracking response times.
- Competitive benchmarking looks outward at direct competitors or industry leaders. This approach is challenging because data can be hard to obtain, but it provides a clear picture of how you stack up in the market. An example is comparing your warehouse picking accuracy with that of a competitor known for fast order fulfilment.
- Strategic benchmarking searches beyond your industry for inspiration. When an escalator manufacturer sought to design escalators for shopping malls, engineers studied mining industry techniques. This broader view can spur innovation.
Some experts also talk about technical benchmarking, which compares specific technologies, tools or methods, and performance benchmarking, which measures overall performance against industry standards. Each type serves a different purpose, but all aim to find best practices that can be adapted to your context.
Steps of Process Benchmarking
Benchmarking works best when you follow a structured approach. Below is a five‑step process, illustrated in the infographic, that you can use for any department or process.
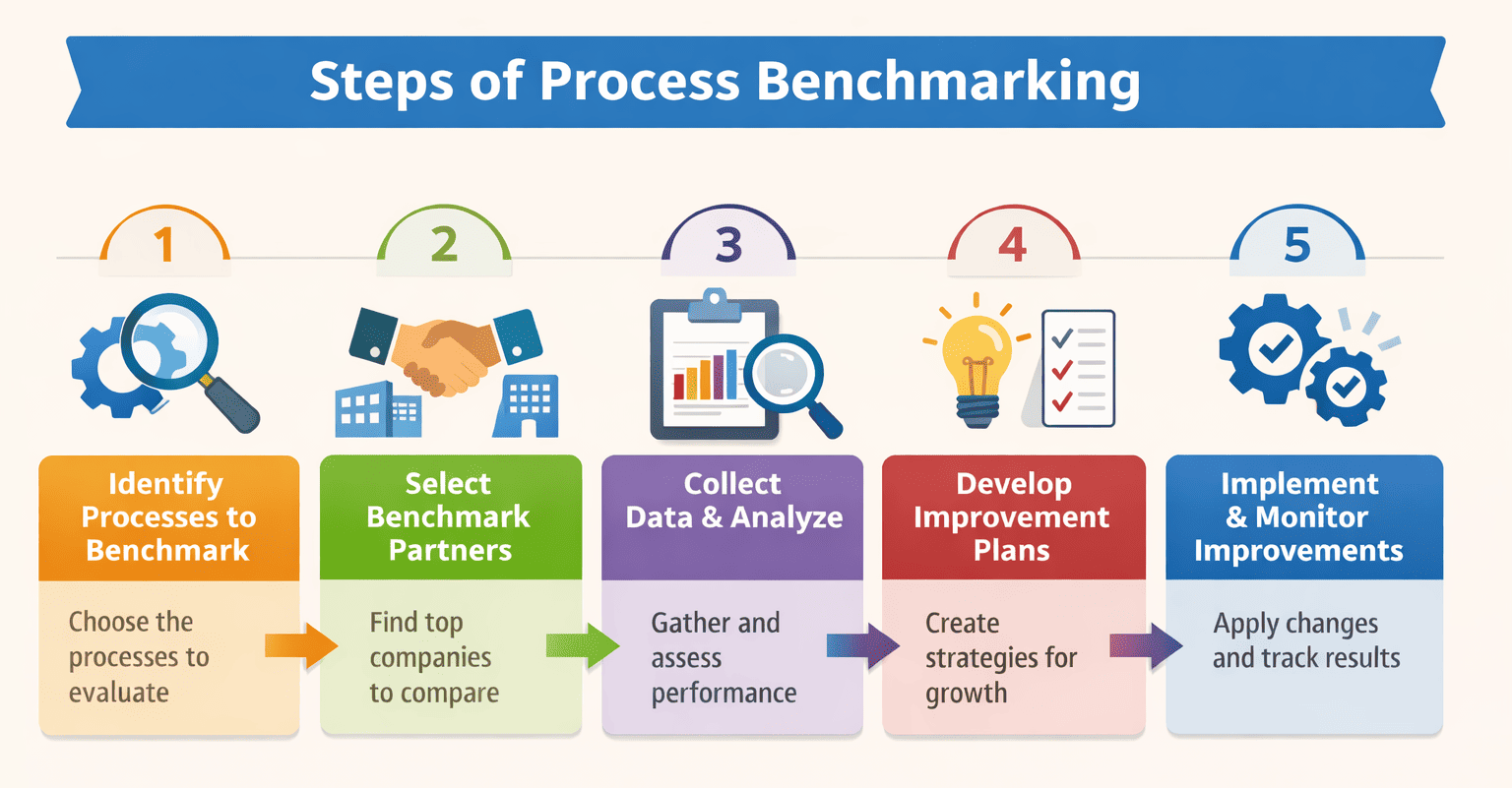
- Identify the process to benchmark: Choose a process that has a significant impact on your business goals. For example, if late shipments are hurting customer satisfaction, focus on order fulfilment. Be specific about the metrics you want to improve, such as cycle time, error rate or cost per unit.
- Select benchmark partners: Decide whom to compare yourself with. Start internally by looking at your best‑performing teams, then expand to competitors or industry leaders. When seeking external data, respect confidentiality and comply with any non‑disclosure agreements.
- Collect and analyze data: Gather quantitative and qualitative information about your process and the benchmark partners. Use interviews, surveys, process maps and performance data. Analyse the differences and identify the practices that lead to superior results.
- Develop improvement plans: Translate insights into practical changes. Create a roadmap that addresses people, technology and workflow. Set specific, measurable targets and assign responsibilities. Ensure buy‑in by involving stakeholders and communicating the benefits.
- Implement and monitor improvements: Put your plan into action and track progress against the benchmarks. Use dashboards and regular reviews to measure results. Adjust strategies based on feedback and continue the benchmarking cycle to maintain momentum.
Pros and Cons of Process Benchmarking
Like any management practice, benchmarking has advantages and drawbacks. Understanding both sides helps you decide if it fits your needs. The infographic below highlights the key points.
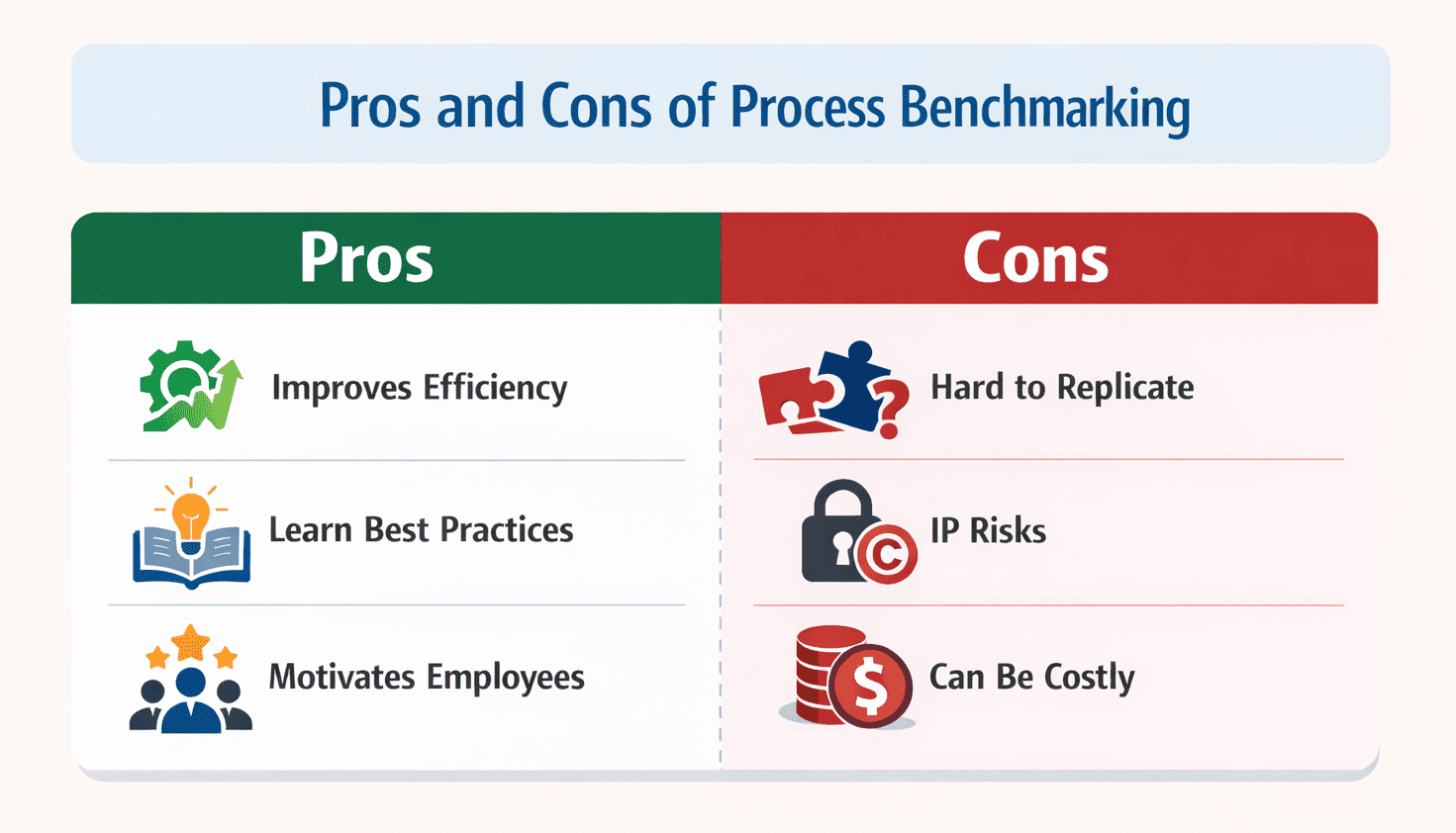
Benefits
Improves efficiency: By discovering how top performers eliminate waste, you learn to streamline your operations. This leads to faster cycle times and lower costs.
Learn best practices: Benchmarking exposes you to new techniques and tools. For example, you might adopt a competitor’s Kanban system to visualise work better.
Motivates employees: When staff see how they stack up against peers, it can inspire friendly competition and a desire to improve.
Drawbacks
Hard to replicate: Best practices are context‑dependent. What works for one company may not fit another due to culture, resources or customer needs.
Intellectual property risks: Sharing sensitive information with external partners can raise confidentiality issues. Always use non‑disclosure agreements and respect proprietary processes.
Can be costly: Collecting and analysing data takes time and resources. Without a clear goal, benchmarking can turn into a costly exercise with little return.
Real‑World Example
Consider a mid‑sized electronics manufacturer struggling with long lead times in its assembly line. The company identified assembly throughput as a key process and decided to benchmark against an industry leader known for lean manufacturing. Managers visited the leader’s facility, observed its use of small‑batch production and cross‑trained teams, and compared cycle times.
They discovered that the leader reduced changeover time by implementing quick‑change tooling and visual controls. After adopting similar practices and training workers, the manufacturer cut its lead time by 20% within six months. This simplified case shows how adapting best practices—not copying them—can yield significant gains.
Best Practices for Successful Benchmarking
- Align with strategy: Benchmark processes that support your most important goals, such as customer satisfaction, cost reduction or innovation. Avoid benchmarking for its own sake.
- Secure leadership support: Management needs to back the project, allocate resources and champion the changes. Without leadership buy‑in, improvements will not stick.
- Respect context: Adapt lessons to your culture and resources. What works in a large, centralised company may not work in a small start‑up.
- Focus on continuous improvement: Use benchmarking as a recurring activity rather than a one‑time project. Regular comparison helps you stay ahead of changing market conditions.
- Protect confidentiality: Use anonymous data sharing and non‑disclosure agreements when exchanging sensitive information with external partners.
FAQs
Q1. What is the first step in process benchmarking?
Identify a process that influences your strategic goals and define the metrics you want to improve. Be specific about what success looks like.
Q2. How often should companies benchmark their processes?
Benchmarking is most effective when done regularly—at least once a year—to ensure your practices stay aligned with industry standards and evolving customer needs.
Q3. Can small businesses benefit from benchmarking?
Yes. Small businesses can benchmark internally to find best practices and externally to learn from industry leaders. Even minor improvements can boost efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
Process benchmarking is a powerful tool for companies committed to continuous improvement. By comparing specific processes against those of industry leaders, you can uncover inefficiencies, adopt proven methods and set realistic goals. Though the practice requires planning and care, the benefits—higher quality, lower costs and motivated teams—often outweigh the challenges. Remember that benchmarking is not about copying competitors; it is about learning and adapting to fit your unique situation.
Ready to make your processes shine? Start by choosing one critical process and ask yourself, “How do our best peers do this better?” Then follow the steps outlined here, monitor progress and celebrate small wins along the way.