Definition: Economic surplus is the sum of the producer surplus and the consumer surplus. It shows the benefits for all involved parties.
This economic metric helps evaluate the market’s health. Economic surplus follows the rule of supply and demand. Businesses want to sell products at a higher price to earn more profit without alienating buyers, and buyers want to buy products at a lower price.
Economic surplus is also known as total welfare, total surplus, or community surplus.
Economic Surplus = Consumer Surplus + Producer Surplus
Consumer Surplus
Here, the product costs less than the price the customer is willing to pay. For example, the customer is willing to pay 20 USD for a product, but the product price is 15 USD. The consumer surplus is the difference between these prices, i.e., 5 USD.
Economic Surplus
Here, the business sells the product at a higher price than they are willing to sell it at. For example, the product cost is 10 USD, and the business is willing to sell it at 12 USD, but they decide to sell it at 15 USD. The producer surplus of 3 USD is the difference between the minimum price and the price they sell.
Equilibrium Position
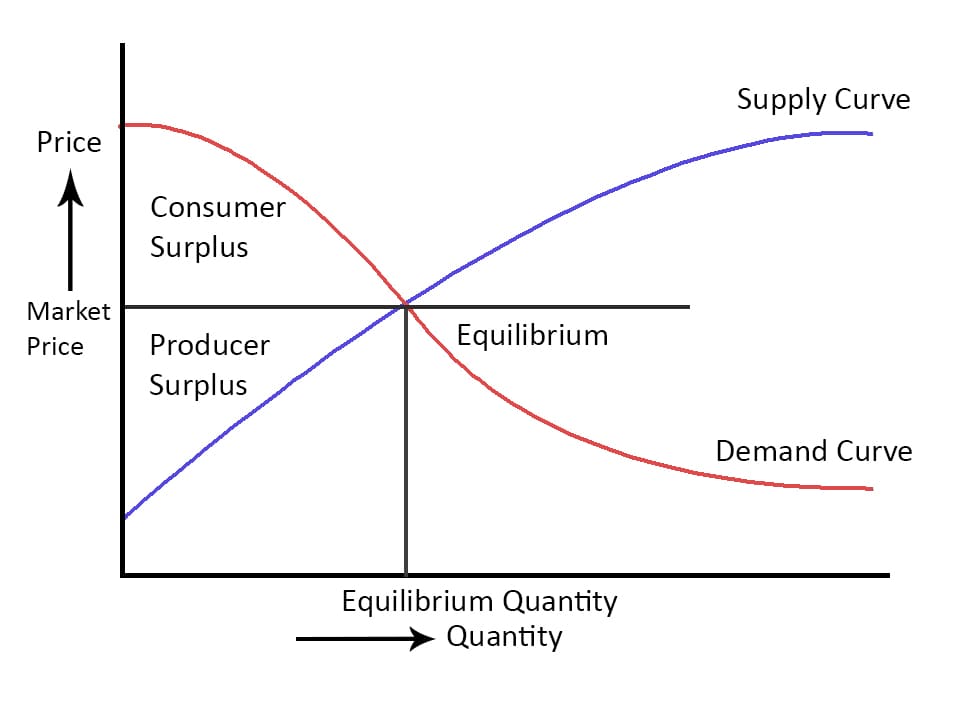
The market is in equilibrium when supply and demand are in good condition. At the equilibrium price, the goals of consumers and producers match (e.g., the consumer is willing to buy the product at a price the consumer is willing to sell).
The consumer surplus benefits the consumers and the producer surplus benefits producers.
Example of Economic Surplus
Let’s say a buyer wants to purchase a PC and is willing to pay 500 USD. While browsing the store, he finds a PC that matches his requirements and costs 400 USD, so he buys it. In this case, the buyer has a 100 USD consumer surplus.
From the producer’s perspective, they were willing to sell the PC for 350 USD but sold them at 400 USD. So, the producer surplus is 50 USD.
The economic surplus for this sale is = 100 + 50
= 150 USD
Cause of Economic Surplus
The law of demand says that the product price increases if the demand falls. However, when the demand for the item increases, the price falls.
The mismatch of supply and demand of a product is the primary cause of economic surplus. It disrupts the market equilibrium and leads to shifts in the product price or quantity produced.
Some factors affecting the economic surplus are:
- Overproduction of the product
- The underproduction of the product
- Regulation and taxes
- Political conditions
Summary
Economic surplus evaluates market conditions and benefits for consumers and producers. Ideally, all parties should get the maximum financial benefits from buying and selling products. The point at which the price stabilizes is the market equilibrium that provides maximum benefits to both parties.
