Formal communication is used to share official information in an organization. No matter your role, you will deal with it when communicating with subordinates, superiors, or colleagues. It follows set rules and ensures clear and professional exchanges of messages.
Understanding formal communication is essential for workplace success and smooth operations. It helps you effectively convey your ideas, instructions, or updates, ensuring everyone stays informed. Formal communication also builds trust and maintains professional relationships.
In this article, I will explain formal communication, why it is important, and how it works. I will also share its types and examples to give you a clear understanding.
What is Formal Communication?
Formal communication is a flow of information through a predefined channel. The information is controlled and deliberately communicated. It flows the hierarchical structure of an organization and follows a proper chain of command.
Formal communication is sharing information within an organization using official channels. It follows a clear structure and specific rules to ensure messages are professional and effective. This type of communication can be written or verbal, such as emails, reports, meetings, or presentations. It helps maintain a clear flow of information between employees, teams, and departments.
Formal communication ensures that everyone understands the message and avoids confusion. It is essential for tasks like giving instructions, sharing updates, or making decisions. This method of communication is often used in workplaces to maintain professionalism and accountability.
Formal communication allows organizations to operate smoothly and achieve their goals. It is also key to building trust and promoting clarity in any professional environment.
Importance of Formal Communication
Formal communication is important because it ensures clarity and professionalism in sharing information. It helps avoid misunderstandings and keeps everyone informed. This type of communication is essential for maintaining order and accountability in an organization.
Formal communication provides a clear record of information, such as plans, decisions, and instructions. It ensures messages are consistent and reach the right people. It also helps build trust among team members and fosters a positive work environment.
Formal communication can improve teamwork, ensure task completion, and help make better decisions. It is also crucial in legal or official matters.
Formal communication supports the smooth and effective operation of any workplace.
Types of Formal Communication
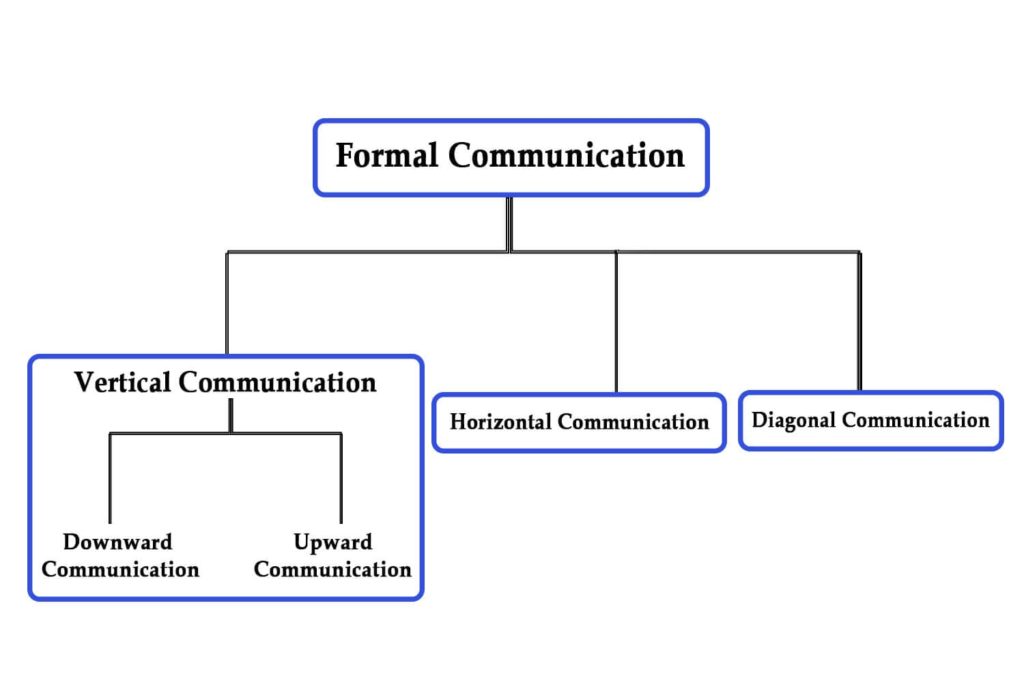
1. Vertical Communication
In vertical communication, information flows between different levels, from top to bottom or bottom to top.
Vertical communication can be:
- Downward Communication
- Upward Communication
Downward Communication
This is the most common communication type in any organization. In this type of communication, information flows from the top to the lower levels, usually in a memo or an email.
This communication is authoritative and intended to get the job done.
It can include notices regarding organizational changes, transfers, promotions, changes in duty, instructions, holidays, and leave.
This communication is mostly formal and written, but it can sometimes be given orally, especially to lower-level workers.
Upward Communication
In upward communication, information flows from lower to upper levels. Generally, this communication comes through a memo or an email. Its purpose is to provide feedback to top management.
This communication type includes responses to management queries, status or progress reports, and resource requests.
2. Horizontal Communication
This communication flows through the same level. Information given between the department or section heads is an example of horizontal communication.
Horizontal communication also occurs within the same section, where it is mostly spoken. Communication between department heads can be oral or written, depending on the requirements.
Horizontal communication is also known as lateral communication.
3. Diagonal Communication
In diagonal communication, information flows between different departments and levels—for example, communication between a department head and a lower-level employee of another section.
Diagonal communication is known as crosswise communication.
Examples of Formal Communication
A few examples of formal communications are:
- Minutes of Meeting (MoM): A written record of discussions and decisions made during a formal meeting. Includes details like attendees, agenda items, action items, and deadlines.
- Memos: Internal official communication used to share updates, requests, or announcements within an organization. Examples: A memo outlining workplace policy changes or project deliverables deadlines.
- Performance Reports: Detailed evaluations of an individual’s or team’s work performance over time. It can include key performance indicators (KPIs), achievements, and areas for improvement.
- Formal Presentations: Structured presentations during business meetings, conferences, or academic settings. Example: Presenting a company’s annual financial report to shareholders.
- Notices: Notices are official documents that inform stakeholders about significant updates or required actions. An example is a notice changing office hours or announcing an upcoming event.
- Contracts and Agreements: Legally binding documents detailing the terms and conditions between parties. Examples are Employment contracts, service agreements, or NDAs.
- Proposals and Reports: Detailed documents outlining strategies, project plans, or business cases. Example: A business proposal for securing new clients or a sustainability report for stakeholders.
- Official Announcements: Used in settings such as schools, offices, or governments to share decisions or updates. Example: Announcing a merger between two companies.
Best Practices for Using Formal Communication
You can use the following best practices while using formal communication:
- Be Clear and Concise: Use straightforward language to convey your message. Avoid jargon unless necessary. Focus on key points and remove unnecessary information.
- Organize Information Effectively: Follow a logical structure, such as introduction, main points, and conclusion. Use headings, bullet points, or numbering to improve readability.
- Follow Established Guidelines: Adhere to your organization’s communication policies and formats. Use templates and checklists to ensure consistency in formal documents.
- Encourage Two-Way Communication: Provide opportunities for feedback, questions, or clarifications. Confirm receipt and understanding of your message when necessary.
- Maintain Professionalism: Use polite, respectful language in all formal communications. Double-check grammar, spelling, and tone before sending or publishing.
- Proofread and Revise: Review your message to eliminate errors and ensure clarity. Seek a second opinion or approval for critical formal communications.
Summary
Formal communication is the structured method organizations use to disseminate information. It adheres to the chain of command, ensuring clarity, accountability, and uniformity in messaging. By following established protocols, formal communication minimizes misunderstandings and supports organizational efficiency. Whether through memos, reports, or official presentations, it helps maintain professionalism and aligns teams with shared goals.
Formal communication is essential for effective collaboration, informed decision-making, and the smooth functioning of any organization.

straight forward and effective
easy to understand
true