Definition: A functional level strategy is a day-to-day plan for organizing routine operations or activities to support an organization’s business and corporate strategies.
Functional level strategies are concerned with tactical decisions, such as human resources, production, operations, marketing, research, development, etc. Each functional department has its own function-level strategies.
A functional level strategy ensures optimum resource utilization inside the department. It facilitates communication and coordination among all other functional units in the organization to support the organization’s corporate and business-level objectives.
Importance of Functional Level Strategy
The functional level strategy has a key role in organizational success as all tasks are performed on this level. It helps develop a daily routine for every section of the organization to carry out activities.
It is a binding element of an organization and establishes coordination among all units of an organization.
According to Michael Porter, a business can have three levels of strategy:
- Corporate Level Strategy
- Business Level Strategy
- Functional Level Strategy
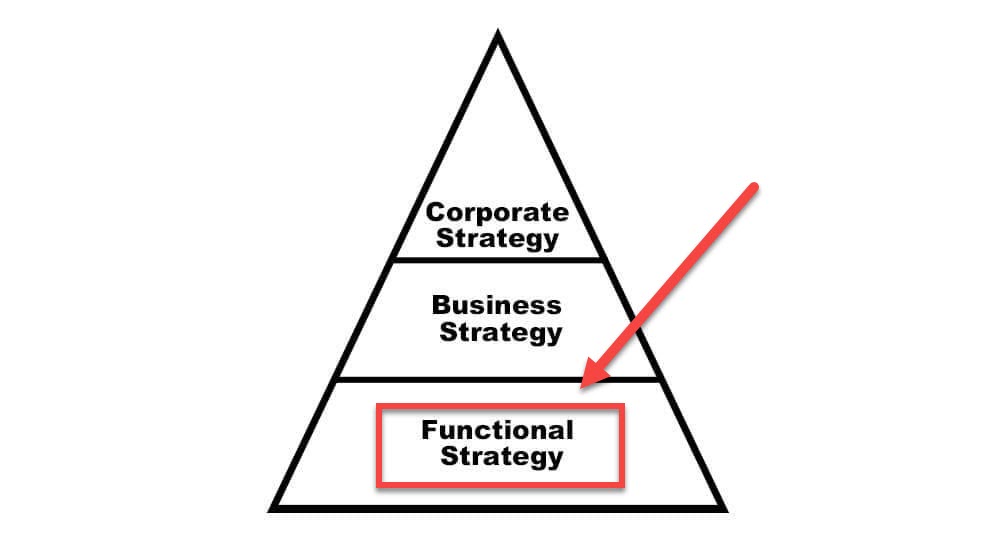
Functional strategy is at the bottom of the Porter pyramid, and today’s article will discuss this strategy in detail.
Types of Functional Level Strategies
The following are the key functional level strategies:
Marketing Strategies
These days, marketing is a key functional level strategy for all organizations.
Marketing helps businesses spread awareness of their product through promotion, collecting leads, and converting them into customers. It does not end here; it constantly markets the product and communicates with customers for future sales.
Financial Strategies
Financial strategies deal with budgeting, expenditures, and monitoring and controlling financial activities. Financial strategies ensure the budget is spent the right way and accounted for.
It also takes care of taxes, shares, dividend payments, etc.
Production Strategies
Product strategies include activities related to the production process. Here, the plan could dictate tasks to be carried out on a daily basis, availability of required materials, testing, etc.
The goal of production strategies is optimal resource utilization, high-quality products, and improved efficiency.
Human Resource Strategies
This deals with activities related to an organization’s workforce.
This can include hiring employees, attendance, leave, indemnity, training, career growth planning, etc.
It ensures the proper office hygiene conditions.
Human resource strategies aim to ensure the required skill power is available at all times and that employees are given opportunities to grow their careers and stay with the organization.
Research & Development Strategies
Research and development play a key role in taking the organization to the next level. These strategies ensure that the organization has competitive and technical advantages over competitors.
The goal of R&D strategies is innovation and improving the product and processes.
New products let organizations create new niches, increase the market share, and diversify the product portfolio.
Continuous improvement and updates in product features ensure the customers’ requirements are met and satisfied at all times.
Examples of Functional Level Strategy
Some examples of a functional level marketing strategy are process efficiency, product quality, delivery at the right time, etc.
Some examples of a human resource are reduced cost in onboarding employees, reduced employee churn rate, employee training, availability of resources, etc.
Summary
Functional level strategies are actions entrusted to each section to carry out their operations that support organizations’ corporate and business level strategies. These strategies let the business achieve the objective of each department.
