As organizations grow, they expand their footprint in different locations and countries. They can enter the market independently or through partnerships. This is where international business strategies come into play and help businesses grow further.
Igor Ansoff was a business manager and mathematician who introduced this strategy as a separate study area through his book “Corporate Strategy,” published in the 1960s.
What is an International Business Strategy?
An international business strategy is an important approach that businesses around the globe undertake to expand internationally. It is a strategic plan that includes essential points about commercial transactions worldwide.
Different countries have different regulations and guidelines, and this strategy helps businesses increase profit in different regions by adapting to each area’s functioning.
An international business strategy covers linguistic barriers, cultural barriers, legal systems, international trade regulations, political barriers, etc.
Four Most Common International Business Strategies
#1 – International Strategy
An international strategy is the basic business strategy that any company willing to expand overseas undertakes. It focuses on an individual point of operation like exporting products and services to different countries or importing products and services from other countries.
This strategy is the easiest and most accessible out of the four, and it is the first choice for any company when they decide to expand to secondary markets globally. The strategy works as an addition to the business’s domestic strategy and expands on the same.
In most cases, the international strategy focuses on an export-oriented business mechanism as it allows businesses to increase sales, expand profits and create opportunities by capturing global markets. The export-driven strategy enables a company to grow faster in international markets and gain more recognition.
A famous example of a company using an international strategy is that of Red Bull. The Austrian company started small in 1987 when they worked as exporting manufacturers. Red Bull witnessed huge growth in their global marketing strategy when they gave out free Red Bull samples to athletes in the US, and their sales went up.
As of 2022, the company is present in 172 countries, covering almost every corner of the world, making around 7.8 billion euros as annual revenue.
Benefits of International Strategy
- It helps businesses test the global appeal of their services and products without huge investments or infrastructural/staffing costs
- The strategy enables companies to simplify their product portfolios based on which product does well globally and cut down on their SKUs
- It opens doors to new revenue potential and sales expansion
- It provides companies with easier access to talent across the globe
- Organizations get an opportunity to absorb new cultures and traditions worldwide, promoting diversity and inclusion
- It exposes companies to foreign direct investments and captures global market shares
- It also immediately helps the business to build a standardized, reputed, and recognizable brand worldwide
#2 – Multi-Domestic Strategy
A multi-domestic strategy is a dynamic strategy as it focuses on achieving the maximum local responsiveness of customers towards the brand through local customization and personalization of products.
Here, businesses tweak their marketing strategies based on the region they are operating in to match national conditions and sentiments. Since every country has different needs and perspectives, organizations incorporate a market strategy that fits the cultural and traditional requirements of the nation.
Businesses twist their taglines, messaging, products, packaging, and customer support based on the target market. This helps them create a localized product or service matching the customers’ preferences.
Businesses employing a multi-domestic strategy have a parent company in the home country. The vision of all subsidiaries in different countries remains the same; only the path to accomplishing the vision is as per local preferences.
Nestle is an example of a multi-domestic strategy. This Switzerland-based company started in 1866 when they only produced milk-based baby food. They introduced other products like milk chocolates, confectionaries, healthcare, and more a few years later.
Currently, Nestle is present in more than 186 countries, with over 2,000 different brands scattered in all regions.
To give an insight into Nestle’s product diversification, the company’s Indian subsidiary, Nestle India, manufactures products like Nestea, Maggi, and Milkybar, which come under the affordable confectionery category for Indian customers.
On the other hand, to cater to vegans, the company has acquired an Israeli firm called Garden Gourmet, which produces vegetarian food products for the UK market.
Benefits of Multi-Domestic Strategy
- It helps companies create a local product portfolio that can be scaled as per their performance
- It strengthens a company’s grounds in local markets more efficiently and quickly
- It decentralizes decisions to ease out operations
- It results in a more substantial local competitive advantage
- It leads to a solid customization mechanism for the business
- It provides businesses with the opportunity to benefit from the low labor costs, local shipping lines, and natural resources available in a particular area
- It helps businesses think outside the box and exploit their potential fully to cater to different regions in different ways
- It gives the company a creative edge over the existing similar products
#3 – Transnational Strategy
A transnational business strategy is a plan of action that focuses equally on global integration and local responsiveness by using almost the same core brand name, values, and product portfolio across international borders. Such businesses operate with a head office in the home country and subsidiaries in global markets.
The strategy helps the business create a solid brand name that reaches out to customers in different parts of the world and provides an effective and efficient center point for operations. In this strategy, companies can also optimize their products and services per local preferences while ensuring that the core brand voice does not get lost in transition.
Businesses employing transnational strategy can give more governance to some specific subsidiaries than others, as per the market conditions and share. The decision-making power lies in the hands of the local branches, making international functioning seamless.
The most popular brand employing a transnational strategy is McDonald’s, which has one of the biggest scalability models worldwide with over 36,000 fast food joints in over 100 countries. McDonald’s adapts the pricing and taste according to the location. However, their core value of selling delicious fast food at affordable pricing remains the same globally.
For example, the McDonald’s chains in India offer a variety of vegetarian food items as most of the Indian population is vegetarian. In contrast, countries like the US, the UAE, Australia, Canada, and others have various meat options and additional items on the menu.
Benefits of Transnational Strategy
- It helps in creating a recognizable, customizable, and accommodating brand across different countries
- As it focuses on local preferences too, it helps businesses connect directly with different cultures to capture market share
- It streamlines and centralizes all operations from a single head office
- It helps businesses make the best use of economies of scale
- It is a highly customer-centric strategy
- It prioritizes customized global standardization and hence is cost-effective
#4 – Global Strategy
A global strategy allows companies to have the maximum global integration with a plan of action that focuses on expanding into global markets.
All companies that employ this strategy aim to cut costs as much as possible, become efficient, and take advantage of economies of scale by offering almost the same product or service portfolio irrespective of the location. Only minor modifications are applied to fit the market, but the overall essence of the business and its offerings remain the same.
Standardization for packaging, product, colors, taglines, messaging, operations, and similar aspects ensure a single brand existence offering a single product portfolio carrying a single message from the parent company. This leads to building a scalable, repeatable, and low-cost process to carry out businesses in foreign markets and penetrating those markets quickly.
The most prominent example of a company employing a global strategy is Apple. The company has over 500 stores across 25 countries worldwide, though the product portfolio remains the same.
There are hardly any modifications that the company deploys based on local preferences. Anything launched in America is launched at all other locations. If Apple launches a new iPhone tomorrow in 4 different colors, they will launch the same phone in all 25 countries with the exact specifications and color variations.
Benefits of Global Strategy
- It makes use of economies of scale to the largest extent
- It helps businesses cut down on costs by not focusing on customizations and personalization
- It helps in streamlining the product development process as there is only a single product line
- Since there are only minimal modifications, the operating process is efficient and seamless
- It builds a specific yet solid brand across all locations
- It enhances the global brand recognition with a single line of product or service
- It allows the company to benefit from the emergence of new markets by raising revenue through higher sales from the same products/services
How to Develop an International Business Strategy in 3 Steps
#1 – Realize Long-Term Goals of the Business & Market Competition
To develop an international business strategy, the company must realize its long-term goals and then decide on expanding overseas.
Suppose the long-term goal of the business is to capture maximum global market share. In that case, an international business strategy focusing on customizing product/service lines per location might be feasible. However, a standardized international strategy is recommended if the company wishes to cut down on costs but boost revenue.
Additionally, understanding market competition and the existence of substitutes helps businesses make an informed decision on expansion strategy.
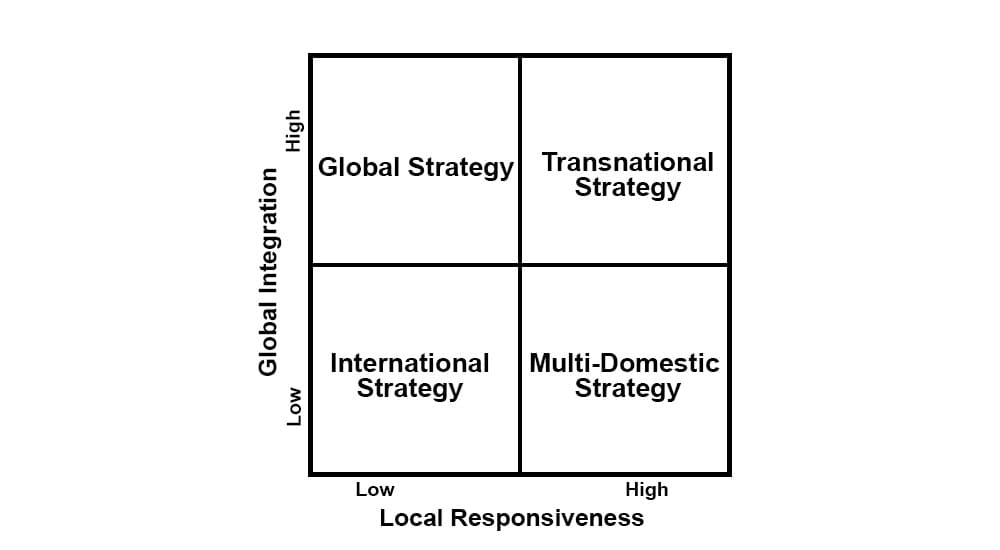
#2 – Understand the Spectrum Between Local Responsiveness and Global Integration
After identifying long-term goals, an organization must analyze the business’s standing on local responsiveness and global integration.
Local responsiveness is how strongly the company is willing to serve specific market needs through customization. Global integration refers to how much the brand focuses on standardizing its products or services as they scale.
The more locally responsive a business is, the more willing it is to change its products or services according to specific markets. The higher a business’s global integration, the higher its willingness to keep the product/service line unchanged.
#3 – Plan the International Organizational Structure and Assemble the Strategy Document
There is a shift in the organizational structure when a business enters international markets. Organizations plan how the parent company and subsidiaries will work along with the specific responsibilities of each division and employee to ensure seamless operations. This plan includes staffing processes, communication channels, barriers (if any), and similar operational needs.
Organizations prepare a written strategy document to outline everything about international expansion. This document mentions threats, opportunities, how the organization plans to achieve healthy global growth, necessary product modifications, and more.
Conclusion
Expanding to international markets brings a business opportunity, a high growth trajectory, and higher sales and revenue. In this era of bolstering globalization, where healthy trade relations are valuable and global presence is a must, it becomes essential for businesses to think and act globally. International business strategies help such companies expand beyond the home country and inflate their market distribution.

In this article, these sentences have some problem (A famous example of a company using an international strategy is that of Red Bull. The Australian company started small in 1987 when they worked as exporting manufacturers).Red Bull is a company in Austria. Not an Australian company.
Corrected.
Thanks Zolin, for pointing out this error.
Surely it is a THAI company! Grating Deng na kap!